摘要
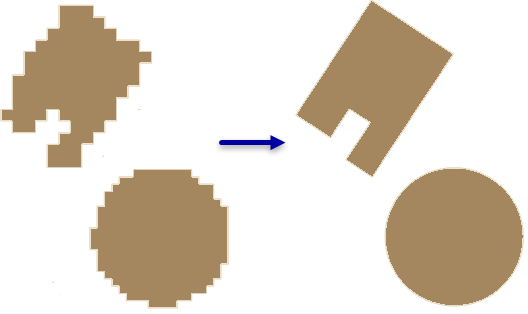
通过消除几何中不需要出现的伪影来对建筑物覆盖区面的形状进行规范化。
插图
用法
此工具通过面压缩算法校正通过要素提取工作流(该工作流可能会产生多余的伪影)创建的建筑物覆盖区面中的变形。
容差值用于定义规则化面必须位于其中的面边界周围的区域。最好可以通过以下方法显示该区域,即先将面的边界转化为线要素,然后根据所需的容差距离缓冲线。
如果您的建筑物覆盖区包含圆形结构,那么应首先处理这些要素。紧凑度可用来识别圆形建筑物。要计算此值,请执行以下操作:
- 添加双精度型字段。
- 使用字段计算器计算以下公式:
(4 * 3.14159265358979 * !shape.area!) / !shape.length! ^ 2 - 一个正圆的值为 1,但由于使用此工具处理的面通常有些不规则,因此,值越接近 1 的形状越有可能是圆形。在使用 CIRCLE 方法执行此工具之前,请先评估结果以识别圆形建筑物的最小值,然后选择大于或等于此值的值。
如果指定参数无法对给定输入生成规则化解决方案,则会将原始要素复制到输出。在 STATUS 字段中指定的值将指示该要素是否已规则化:
- 0 - 规则化要素
- 1 - 原始要素
语法
RegularizeBuildingFootprint_3d (in_features, out_feature_class, method, tolerance, densification, precision, diagonal_penalty, min_radius, max_radius)
| 参数 | 说明 | 数据类型 |
in_features | 表示建筑物覆盖区的待规则化面。 | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | 将由此工具生成的要素类。 | Feature Class |
method | 在输入要素处理过程中要使用的规则化方法。
| String |
tolerance | 规则化覆盖区可从其原始要素的边界偏移的最大距离。指定的值将基于输入要素坐标系的线性单位。 | Double |
densification | 用于评估规则化要素为直的或弯的采样间隔。增密必须小于等于容差值。 此参数仅用于支持直角标识的方法。 | Double |
precision | 空间格网在规则化过程中使用的精度。值的有效范围为 0.05 到 0.25。 | Double |
diagonal_penalty | 控制创建直角连接时的距离偏差。将使用小于对角惩罚系数的距离创建直角。 此参数仅用于 RIGHT_ANGLES_AND_DIAGONALS 方法。 | Double |
min_radius | 规则化圆可具有的最小半径。值 0 表示无最小尺寸限制。此选项仅适用于 CIRCLE 方法。 | Double |
max_radius | 规则化圆可具有的最大半径。此选项仅适用于“圆形”方法。 | Double |
代码示例
RegularizeBuildingFootprint 示例 1(Python 窗口)
下面的示例演示了如何在 Python 窗口中使用此工具。
arcpy.env.workspace = 'c:/data'
arcpy.ddd.RegularizeBuildingFootprint('rough_footprints.shp',
'regularized_footprints.shp',
method='Circle', tolerance=1.5, min_radius=10,
max_radius=20)
RegularizeBuildingFootprint 示例 2(独立脚本)
下面的示例演示了如何在独立 Python 脚本中使用此工具。
'''****************************************************************************
Name: Classify Lidar & Extract Building Footprints
Description: Extract footprint from lidar points classified as buildings,
regularize its geometry, and calculate the building height.
****************************************************************************'''
import arcpy
lasd = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
dem = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1)
footprint = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2)
try:
desc = arcpy.Describe(lasd)
if desc.spatialReference.linearUnitName in ['Foot_US', 'Foot']:
unit = 'Feet'
else:
unit = 'Meters'
ptSpacing = desc.pointSpacing * 2.25
sampling = '{0} {1}'.format(ptSpacing, unit)
# Classify overlap points
arcpy.ddd.ClassifyLASOverlap(lasd, sampling)
# Classify ground points
arcpy.ddd.ClassifyLasGround(lasd)
# Filter for ground points
arcpy.management.MakeLasDatasetLayer(lasd, 'ground', class_code=[2])
# Generate DEM
arcpy.conversion.LasDatasetToRaster('ground', dem, 'ELEVATION',
'BINNING NEAREST NATURAL_NEIGHBOR',
sampling_type='CELLSIZE',
sampling_value=desc.pointSpacing)
# Classify noise points
arcpy.ddd.ClassifyLasNoise(lasd, method='ISOLATION', edit_las='CLASSIFY',
withheld='WITHHELD', ground=dem,
low_z='-2 feet', high_z='300 feet',
max_neighbors=ptSpacing, step_width=ptSpacing,
step_height='10 feet')
# Classify buildings
arcpy.ddd.ClassifyLasBuilding(lasd, '7.5 feet', '80 Square Feet')
#Classify vegetation
arcpy.ddd.ClassifyLasByHeight(lasd, 'GROUND', [8, 20, 55],
compute_stats='COMPUTE_STATS')
# Filter LAS dataset for building points
lasd_layer = 'building points'
arcpy.management.MakeLasDatasetLayer(lasd, lasd_layer, class_code=[6])
# Export raster from lidar using only building points
temp_raster = 'in_memory/bldg_raster'
arcpy.management.LasPointStatsAsRaster(lasd_layer, temp_raster,
'PREDOMINANT_CLASS', 'CELLSIZE', 2.5)
# Convert building raster to polygon
temp_footprint = 'in_memory/footprint'
arcpy.conversion.RasterToPolygon(temp_raster, temp_footprint)
# Regularize building footprints
arcpy.ddd.RegularizeBuildingFootprint(temp_footprint, footprint,
method='RIGHT_ANGLES')
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
环境
许可信息
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: 需要 3D Analyst