摘要
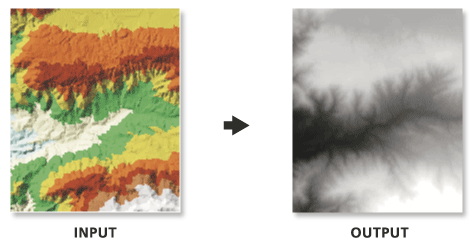
通过在指定采样距离处插入输入 TIN 高程值中的栅格像元值的方式创建栅格。
插图
用法
由于以均匀的间隔对输入 TIN 表面进行插值,因此输出栅格中可能会出现信息的丢失。栅格是否能够准确地表示 TIN 将取决于栅格的分辨率及 TIN 表面的变化程度和间隔。通常,分辨率越高,输出栅格就越能准确地表示 TIN 表面。因为栅格是像元结构,所以它无法保持可能出现在输入 TIN 中的硬隔断线和软隔断线的边。
-
导出较大栅格时,如果使用整型数据可以满足 z 值的精度要求,则考虑将输出数据类型指定为整型以节省磁盘空间。
语法
TinRaster_3d (in_tin, out_raster, {data_type}, {method}, {sample_distance}, {z_factor})| 参数 | 说明 | 数据类型 |
in_tin | 待处理的 TIN 数据集。 | TIN Layer |
out_raster | 输出栅格的位置和名称。在向地理数据库或文件夹(如 Esri Grid)中存储栅格数据集时,不应向栅格数据集的名称添加文件扩展名。在将栅格存储到文件夹中时,可提供文件扩展名以定义栅格的格式,例如 .tif(生成 GeoTIFF)或 .img(生成 ERDAS IMAGINE 格式文件)。 如果栅格存储为 TIFF 文件或存储在地理数据库中,可使用地理处理环境设置指定其栅格压缩类型和质量。 | Raster Dataset |
data_type (可选) | 可通过以下关键字定义输出栅格的数据类型:
| String |
method (可选) | 该插值方法用于创建栅格。
| String |
sample_distance sampling_method distance (可选) | 用于定义输出栅格的像元大小的采样方法和距离。 | String |
z_factor (可选) | Z 值将乘上的系数。此值通常用于转换 Z 线性单位来匹配 XY 线性单位。默认值为 1,此时高程值保持不变。如果输入表面的空间参考具有已指定线性单位的 Z 基准,则将禁用此参数。 | Double |
代码示例
TinRaster 示例 1(Python 窗口)
下面的示例演示了如何在 Python 窗口中使用此工具。
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.TinRaster_3d("tin", "raster.img", "INT", "LINEAR", "OBSERVATIONS 250", 1)
TinRaster 示例 2(独立脚本)
下面的示例演示了如何在独立 Python 脚本中使用此工具。
'''******************************************************************
Name: TinRaster Example
Description: This script demonstrates how to use the
TinRaster tool to create rasters from
each TIN in the target workspace.
******************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
import exceptions, sys, traceback
try:
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Set environment setting
env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set Local Variables
dataType = "INT"
method = "NATURAL_NEIGHBORS"
sampling = "CELLSIZE 10"
zfactor = "1"
# Create list of TINs
TINList = arcpy.ListDatasets("*", "Tin")
# Verify the presence of TINs in the list
if TINList:
# Iterate through the list of TINs
for dataset in TINList:
# Define the name of the output file
outRaster = "{0}_natural.img".format(dataset)
# Execute TinRaster
arcpy.ddd.TinRaster(dataset, outRaster, dataType,
method, sampling, zfactor)
print "Finished."
else:
print "There are no TIN(s) in {0}.".format(env.workspace)
arcpy.CheckInExtension("3D")
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = 'PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}'\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = 'ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n'.format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
环境
许可信息
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: 需要 3D Analyst