Description
A compromise projection used for world maps that averages the coordinates from the equirectangular (equidistant cylindrical) and Aitoff projections. Developed by Oswald Winkel in 1921.
- Learn about the equirectangular (equidistant cylindrical) projection
- Learn about the Aitoff projection
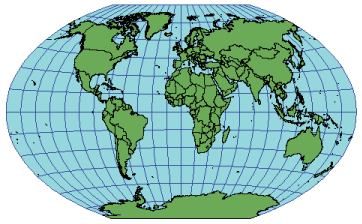
Projection method
Modified azimuthal—coordinates are the average of the Aitoff and equirectangular projections. Meridians are equally spaced and concave toward the central meridian. The central meridian is a straight line. Parallels are equally spaced curves, concave toward the poles. The poles are approximately 0.4 times the length of the equator. The length of the poles depends on the standard parallel chosen.
Linear graticules
The equator and the central meridian.
Properties
Shape
Shape distortion is moderate. In the polar regions along the outer meridians, the distortion is severe.
Area
Distortion is moderate. In the polar regions along the outer meridians, the distortion is severe.
Direction
Generally distorted.
Distance
Generally, scale is made true along latitudes 50.467° N and S or 40° N and S. The second case is used by Bartholomew Ltd., a British mapmaking company.
Limitations
Neither conformal nor equal area. Useful only for world maps.
Uses and applications
Developed for use in general and thematic world maps.
Used by the National Geographic Society since 1998 for general and thematic world maps.
Parameters
Desktop
- False Easting
- False Northing
- Central Meridian
- Standard Parallel 1
Workstation
- Radius of the sphere of reference
- Longitude of Central Meridian
- Latitude of standard parallel
- False Easting (meters)
- False Northing (meters)