Summary
Creates a new feature class of ring trade area features. The radii are determined by a field in the ring center (store) layer.
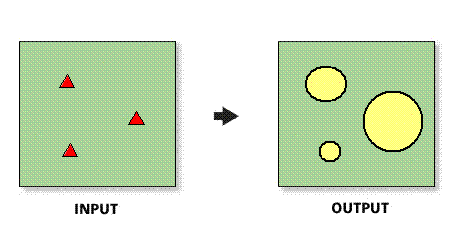
Illustration
Usage
The spatial reference of the output feature class will be the same as the store layer.
The input Store Layer must be point features.
In most cases, the input Store Layerwill be a Business Analyst store layer.
Selecting ALL in the Sites to use parameter will create rings for each point feature in the input Store Layer
If Remove Overlap is checked, Thiessen polygons are used to remove overlap between output ring polygons.
The Value per unit field determines the data value used to set the threshold for your rings, must be numeric, and cannot be negative.
If your Store Layer contains a field that has actual radii for each store point, set the value per unit to one.
Syntax
DataDrivenRings_ba (InputFeatureLayer, IDField, All_Or_Single_Or_Selected, RadiusFieldName, ValuePerUnit, {MeasureUnits}, OutputFeatureClass, {ByID_Or_ByName}, {Single_Site}, {RemoveOverlap}, {ExpValue})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
InputFeatureLayer | The input feature class containing center points for the rings. In most cases, this will be a Business Analyst store layer. | Feature Class |
IDField | Unique ID field in the ring center (store) layer. | Field |
All_Or_Single_Or_Selected | Creates rings for points in the input feature layer.
| String |
RadiusFieldName | Field used to determine radii of the rings. | Field |
ValuePerUnit | Value entered proportional to one measured unit. For example, $450,000 in sales is equal to 1 mile. | Double |
MeasureUnits (Optional) | The units used with the distance values. By default, the units defined in the Business Analyst preferences will be selected.
| String |
OutputFeatureClass | The feature class that will contain the ring features. | Feature Class |
ByID_Or_ByName (Optional) | Field used to select a single point.
| String |
Single_Site (Optional) | ID or name of store used as the single point. | String |
RemoveOverlap (Optional) | Creates overlapping concentric rings or removes overlap.
| Boolean |
ExpValue (Optional) | An exponent value to determine the size of the data-driven rings. This exponent is the same type of exponent used in the Huff Modeling. | Double |
Code Sample
DataDrivenRings Example (Stand-alone Script)
# Name: DataDrivenRings.py
# Description: Creates ring based trade areas in San Francisco based on sales values in a store layer.
# Author: Esri
# Import system modules
import arcview
import arcpy
arcpy.AddToolbox("C:\Program Files (x86)\ArcGIS\Desktop10.3\Business Analyst\ArcToolbox\Toolboxes\Business Analyst Tools.tbx")
try:
# Acquire extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Business")
# Define input and output parameters for the Data Driven Rings tool
sStorePath = "C:/temp/sf_store.shp"
sIdFld = "STORE_ID"
sOutPath = "C:/temp/RingOutput.shp"
sRadiusFld = "SALES"
# Create data driven rings trade areas
arcpy.DataDrivenRings_ba(StorePath, IdFld, "ALL", RadiusFld, "450000", "Miles", OutPath)
# Release extension license
arcpy.CheckInExtension("Business")
except:
print arcpy.GetMessages(2)
Environments
This tool does not use any geoprocessing environments
Licensing Information
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requires Business Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requires Business Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requires Business Analyst