Available with 3D Analyst license.
A terrain dataset is a multiresolution, TIN-based surface built from measurements stored as features in a geodatabase. They're typically made from lidar, sonar, and photogrammetric sources. Terrains reside in the geodatabase, inside feature datasets with the features used to construct them.
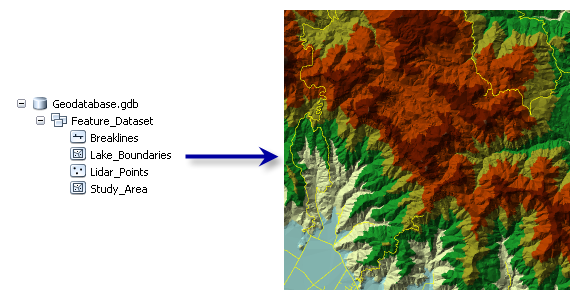
Terrains have participating feature classes and rules, similar to topologies. Common feature classes that act as data sources for terrains include the following:
- Multipoint feature classes of 3D mass points created from a data source such as lidar or sonar
- 3D point and line feature classes created on photogrammetric workstations using stereo imagery
- Study area boundaries used to define the bounds of the terrain dataset
The terrain dataset's rules control how features are used to define a surface. For example, a feature class containing edge of pavement lines for roads could participate with the rule that its features be used as hard breaklines. This will have the desired effect of creating linear discontinuities in the surface.
Rules also indicate how a feature class participates through a range of scales. Edge of pavement features might only be needed for medium- to large-scale surface representations. Rules could be used to exclude them from use at small scales, which would improve performance.
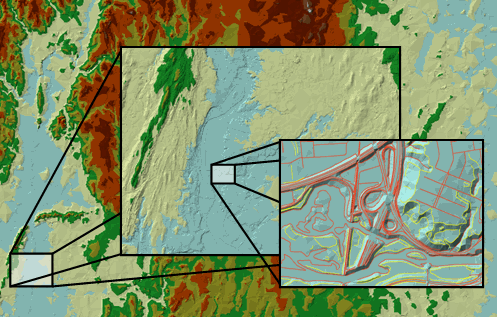
A terrain dataset in the geodatabase references the original feature classes. It doesn't actually store a surface as a raster or TIN. Rather, it organizes the data for fast retrieval and derives a TIN surface on the fly. This organization involves the creation of terrain "pyramids" that are used to quickly retrieve only the data necessary to construct a surface of the required level of detail (LOD) for a given area of interest (AOI) from the database. The appropriate pyramid level is used relative to the current display scale or can be chosen by the user in analysis functions, so the appropriate level of resolution is used to satisfy accuracy requirements.
The terrain dataset, along with its collection of supporting tools, facilitates the storage and maintenance of vector-based surface measurements coupled with the ability to use surfaces derived from those measurements. Geoprocessing functions are provided to load data from external sources into geodatabase feature classes. Editing and geodatabase tools are used to maintain and update the data over time. Interactive display and query tools provide the means to explore and use terrain surfaces. TINs and rasters can be extracted from terrains based on area of interest (AOI) and level of detail (LOD). The suite of tools provides a comprehensive means of surface production and use.
An overview of working with terrain datasets in ArcGIS
If you have data sources such as stereo-captured photogrammetric features and mass point collections of 3D data such as lidar, sonar, and bathymetry, chances are that using terrain datasets in the geodatabase can help you better manage this information.
There is increasing use of lidar and other sensors for collecting high-resolution and massively large point datasets of elevation observations. Geodatabases are useful for managing these critical data assets as well as for integrating these and other data sources into terrain datasets.
Terrain datasets will help you with the following:
- Better represent and model the terrain of study areas by integrating 3D-based mass point observations with other data sources such as 3D features captured using stereo photogrammetry.
- Perform many types of 3D spatial analysis in your GIS using the ArcGIS 3D Analyst.
- Derive raster-based digital elevation models for use in modeling and analysis systems such as the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst.
Terrains include pyramids that provide the appropriate levels of detail for use at multiple scales.
The table below has links to key information about ArcGIS support for terrain datasets including a number of common workflows for building and using terrains in ArcGIS.
Terrain dataset tasks
| Tasks | Links for more information |
|---|---|
Designing a terrain dataset | |
Creating a set of feature classes within a common feature dataset in a geodatabase | |
Loading 3D data into feature classes | |
Building a terrain dataset using ArcCatalog or the Catalog window | See Building a terrain dataset using the New Terrain wizard. |
Building a terrain dataset using geoprocessing tools | |
Drawing and displaying terrain datasets | |
Using terrain datasets in ArcGlobe and ArcScene | |
Managing updates to terrain datasets and their feature class data sources | |
Managing terrains in a versioned geodatabase |