Available with 3D Analyst license.
Summary
Creates a shaded relief from a surface raster by considering the illumination source angle and shadows.
Illustration
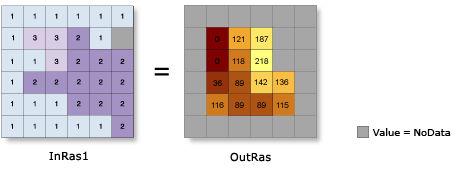
Usage
The Hillshade tool creates a shaded relief raster from a raster. The illumination source is considered to be at infinity.
The hillshade raster has an integer value range of 0 to 255.
Two types of shaded relief rasters can be output. If the Model shadows option is disabled (unchecked), the output raster only considers local illumination angle. If it is enabled (checked), the output raster considers the effects of both local illumination angle and shadow.
The analysis of shadows is done by considering the effects of the local horizon at each cell. Raster cells in shadow are assigned a value of zero.
-
To create a raster of the shadow areas only, use the Reclassify tool to separate the value zero from the other hillshade values. The Model shadows option must be enabled (checked) to create this result.
If the input raster is in a spherical coordinate system, such as decimal degrees, the resulting hillshade may look peculiar. This is due to the difference in measure between the horizontal ground units and the elevation z units. Since the length of a degree of longitude changes with latitude, you will need to specify an appropriate z-factor for that latitude. If your x,y units are decimal degrees and your z units are meters, some appropriate z-factors for particular latitudes are:
Latitude Z-factor 0 0.00000898 10 0.00000912 20 0.00000956 30 0.00001036 40 0.00001171 50 0.00001395 60 0.00001792 70 0.00002619 80 0.00005156You can create dramatic three-dimensional views of the hillshaded surface by draping the output raster using ArcGIS ArcScene.
When the input raster needs to be resampled, the bilinear technique will be used. An example of when an input raster may be resampled is when the output coordinate system, extent, or cell size is different from that of the input.
Syntax
Hillshade_3d (in_raster, out_raster, {azimuth}, {altitude}, {model_shadows}, {z_factor})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The input surface raster. | Raster Layer |
out_raster | The output hillshade raster. The hillshade raster has an integer value range of 0 to 255. | Raster Dataset |
azimuth (Optional) | Azimuth angle of the light source. The azimuth is expressed in positive degrees from 0 to 360, measured clockwise from north. The default is 315 degrees. | Double |
altitude (Optional) | Altitude angle of the light source above the horizon. The altitude is expressed in positive degrees, with 0 degrees at the horizon and 90 degrees directly overhead. The default is 45 degrees. | Double |
model_shadows (Optional) | Type of shaded relief to be generated.
| Boolean |
z_factor (Optional) | Number of ground x,y units in one surface z-unit. The z-factor adjusts the units of measure for the z-units when they are different from the x,y units of the input surface. The z-values of the input surface are multiplied by the z-factor when calculating the final output surface. If the x,y units and z-units are in the same units of measure, the z-factor is 1. This is the default. If the x,y units and z-units are in different units of measure, the z-factor must be set to the appropriate factor, or the results will be incorrect. For example, if your z-units are feet and your x,y units are meters, you would use a z-factor of 0.3048 to convert your z-units from feet to meters (1 foot = 0.3048 meter). | Double |
Code sample
Hillshade example 1 (Python window)
This example generates a hillshade raster that includes shadows. Specific azimuth and altitude angles are set.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.HillShade_3d("elevation", "C:/output/outhillshd01", 180, 75, "SHADOWS", 1)
Hillshade example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example generates a hillshade raster that includes shadows. Specific azimuth and altitude angles are set and a z-factor is used to convert z-units from feet to meters.
# Name: HillShade_3d_Ex_02.py
# Description: Computes hillshade values for a raster surface.
# Requirements: 3D Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "elevation"
outRaster = "C:/output/outhillshd02"
azimuth = 180
altitude = 75
modelShadows = "SHADOWS"
zFactor = 0.348
# Check out the ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Execute HillShade
arcpy.HillShade_3d(inRaster, outRaster, azimuth, altitude,
modelShadows, zFactor)
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst