Available with 3D Analyst license.
Summary
Identifies which observer points are visible from each raster surface location.
Illustration
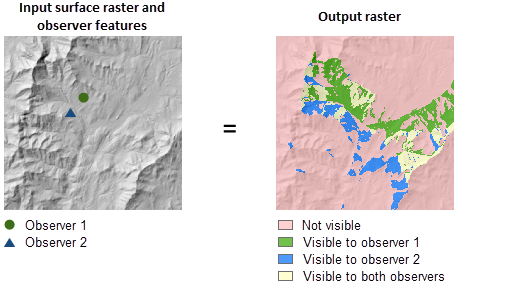
Usage
Determining observer points is a computer-intensive process. The processing time is dependent on the resolution. For preliminary studies, you may want to use a coarser cell size to reduce the number of cells in the input. Use the full-resolution raster when the final results are ready to be generated.
-
If the input raster contains undesirable noise caused by sampling errors, and you have the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension available, you can smooth the raster with a low-pass filter, such as the Mean option of Focal Statistics, before running this tool.
The visibility of each cell center is determined by comparing the altitude angle to the cell center with the altitude angle to the local horizon. The local horizon is computed by considering the intervening terrain between the point of observation and the current cell center. If the point lies above the local horizon, it is considered visible.
An optional above ground level (AGL) output raster is provided by the tool. Each cell on the AGL output raster records the minimum height that needs to be added to that cell to make it visible by at least one observer.
When the input observer features contain multiple observers, the output value is the minimum of the AGL values from all of the individual observers.
When the input raster needs to be resampled, the bilinear technique will be used. An example of when an input raster may be resampled is when the output coordinate system, extent, or cell size is different from that of the input.
Syntax
ObserverPoints_3d (in_raster, in_observer_point_features, out_raster, {z_factor}, {curvature_correction}, {refractivity_coefficient}, {out_agl_raster})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The input surface raster. | Raster Layer |
in_observer_point_features | The point feature class that identifies the observer locations. The maximum number of points allowed is 16. | Feature Layer |
out_raster | The output raster. The output identifies exactly which observer points are visible from each raster surface location. | Raster Dataset |
z_factor (Optional) | Number of ground x,y units in one surface z-unit. The z-factor adjusts the units of measure for the z-units when they are different from the x,y units of the input surface. The z-values of the input surface are multiplied by the z-factor when calculating the final output surface. If the x,y units and z-units are in the same units of measure, the z-factor is 1. This is the default. If the x,y units and z-units are in different units of measure, the z-factor must be set to the appropriate factor, or the results will be incorrect. For example, if your z-units are feet and your x,y units are meters, you would use a z-factor of 0.3048 to convert your z-units from feet to meters (1 foot = 0.3048 meter). | Double |
curvature_correction (Optional) | Allows correction for the earth's curvature.
| Boolean |
refractivity_coefficient (Optional) | Coefficient of the refraction of visible light in air. The default value is 0.13. | Double |
out_agl_raster (Optional) | The output above ground level (AGL) raster. The AGL result is a raster where each cell value is the minimum height that must be added to an otherwise nonvisible cell to make it visible by at least one observer. Cells that were already visible will have a value of 0 in this output raster. | Raster Dataset |
Code sample
ObserverPoints example 1 (Python window)
This example identifies exactly which observer points are visible from each raster surface location.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.ObserverPoints_3d("elevation","observers.shp", "C:/output/outobspnt01",
1, "CURVED_EARTH", 0.13)
ObserverPoints example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example identifies exactly which observer points are visible from each raster surface location.
# Name: ObserverPoints_3d_Ex_02.py
# Description: Identifies exactly which observer points are visible
# from each raster surface location.
# Requirements: 3D Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "elevation"
inObsPoints = "observers.shp"
outRaster = "C:/output/outobspnt02"
zFactor = 1
useEarthCurv = "CURVED_EARTH"
refractionVal = 0.13
# Check out the ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Execute ObserverPoints
arcpy.ObserverPoints_3d(inRaster, inObsPoints, outRaster, zFactor,
useEarthCurv, refractionVal)
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst or Spatial Analyst