Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Calculates the inverse tangent of cells in a raster.
Illustration
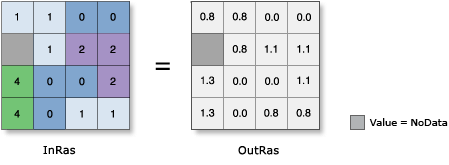
Usage
In mathematics, all Trigonometric functions have a defined range of valid input values, called the domain. The output values from each function also has a defined range. For this tool
The Domain is : -∞ < [in_value] < ∞
The Range is : -pi/2 ≤ [out_value] ≤ pi/2
Note that here -∞ and ∞ represent the smallest negative and largest positive value supported by the particular raster format, respectively.
The input values to this tool are interpreted as unitless.
Output values are always floating point, regardless of the input data type.
The output values from this tool are in radians. If degrees are desired, the resulting raster must be multiplied by the radians-to-degrees conversion factor of 180/pi, or approximately 57.296.
For further assistance, a procedure to follow and some examples of converting output in radians to degrees are available.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
ATan (in_raster_or_constant)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant | The input for which to calculate the inverse tangent values. In order to use a number as an input for this parameter, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. The values are the inverse tangent of the input values. | Raster |
Code sample
ATan example 1 (Python window)
This example calculates the inverse tangent of the values in the input Grid raster.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outATan = ATan("degs")
outATan.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outatan")
ATan example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example calculates the inverse tangent of the values in the input Grid raster and outputs a TIFF raster.
# Name: ATan_Ex_02.py
# Description: Calculates the inverse tangent of cells in a raster
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "degs"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute ATan
outATan = ATan(inRaster)
# Save the output
outATan.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outatan.tif")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst