Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Performs a Boolean And operation on the cell values of two input rasters.
If both input values are true (non-zero), the output value is 1. If one or both inputs are false (zero), the output is 0.
Illustration
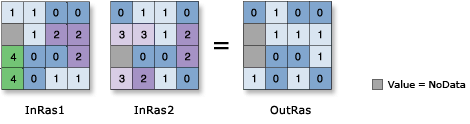
Usage
The Boolean math tools interpret the inputs as Boolean values, where nonzero values are considered true, and zero is considered false.
Two inputs are necessary for this Boolean evaluation to take place.
The order of inputs is irrelevant for this tool.
If the input values are floating point, they are converted to integer values of either 0 or 1 before the operation is performed. If the input value is a floating point 0.0, it is converted to an integer 0. If the input is any value other than 0.0, it is converted to be an integer 1. For example, input float values of 0.6, 32.22 and -4.2 will all be treated as being 1. The output values are always integer.
In Map Algebra, the equivalent operator symbol for this tool is "&" (link).
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
BooleanAnd (in_raster_or_constant1, in_raster_or_constant2)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant1 | The first input to use in this Boolean operation. A number can be used as an input for this parameter, provided a raster is specified for the other parameter. To be able to specify a number for both inputs, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
in_raster_or_constant2 | The second input to use in this Boolean operation. A number can be used as an input for this parameter, provided a raster is specified for the other parameter. To be able to specify a number for both inputs, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. The output values will be either 0 or 1. | Raster |
Code sample
BooleanAnd example 1 (Python window)
This example performs a Boolean And operation on two Grid rasters and outputs the result as an IMG raster.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outBooleanAnd = BooleanAnd("degs", "negs")
outBooleanAnd.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outbooland.img")
BooleanAnd example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example performs a Boolean And operation on two Grid rasters.
# Name: BooleanAnd_Ex_02.py
# Description: Performs a Boolean And operation on the cell values
# of two input rasters
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster1 = "degs"
inRaster2 = "negs"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute BooleanAnd
outBooleanAnd = BooleanAnd(inRaster1, inRaster2)
# Save the output
outBooleanAnd.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outbooland")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst