This topic gets you started in creating a simple strip map.
A strip map is a set of map pages that follow a route, such as a river, road, or pipeline. Each page of the map shows a defined geographic area on either side of the line feature. Each subsequent page in a strip map shows the area further down the line. Often, there is a bit of geographic overlap between adjacent map pages. The direction of north on the page shifts so that the flow of map is kept constant. A strip map can be quickly defined in ArcMap using Data Driven Pages and exported via the export map dialog box.
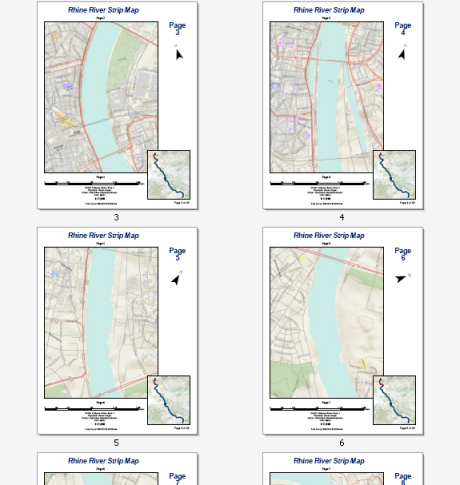
The example above shows a strip map for the Rhine River between the cities of Köln and Koblenz. This 44-page series can be easily created by any ArcMap user with an Internet connection. The data comes from the World Topographic map service available at ArcGIS Online. You can easily re-create this strip map using Data Driven Pages, the geoprocessing tools available from the Data Driven Pages toolset, data frame properties, and dynamic text. You will need to create the line feature used to determine the route of the strip map. This can be done by creating a new line feature class using the ArcMap editing tools.
Before you create a strip map, you need to start with a map and page layout. The strip map above is a letter page size (8.5 by 11 inches) with a portrait orientation. The map will have a title, north arrow, scale bars, text for the map's projection, and labels for the next page and the previous page.
In order to get the most accurate results the map needs to be in an appropriate projection. DHDN 3 Degree Gauss Zone 2 is appropriate for this area.
- Start ArcMap.
- Click File > ArcGIS Online and add the World Topographic map service. You may have to search for the service.
- Open the Find tool
 and click the Locations tab.
and click the Locations tab. - Click the Choose a Locator arrow and choose World Places (ArcGIS Online).
- Type Koln in the PlaceName text box.
- Click Find.
- Right-click the result and choose Zoom to.
- Close the Find dialog box.
- Double-click the default data frame Layers and click the General tab on the Data Frame Properties dialog box.
- Click the Size and Position tab.
- For position, enter 0.5 for the x position and 2.0 for the y position.
- For size, enter 6.0 for Width and 8.0 for Height (these values will be used in a later step).
- Click the Coordinate System tab.
- Type DHDN 3 Degree Gauss Zone 2 in the search text box and press enter.
- Expand the resulting folder and choose DHDN 3 Degree Gauss Zone 2.
- Click OK.
A line feature class is needed to create the strip map index features that define the geographic boundaries of each page in the series. Odds are you don't have line features following the Rhine River. That's okay. You can easily create this line feature class yourself using ArcMap's editing tools. The line will not be used in the map so it doesn't matter how the line is rendered in the map. The images below show the start and end of the line feature class.
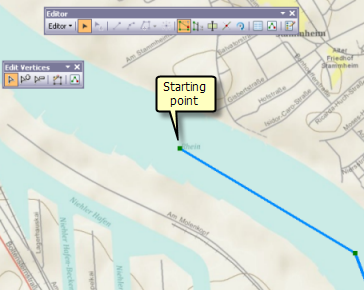
As long as you get close to replicating the start and end points and digitize your line within the boundaries of the river, you should end up with a line that can come very close to replicating the sample strip map above. For future reference, give this line feature class the name Upper Rhine.
For more information on editing, see
- What is editing?
- A quick tour of editing
- How to enable editing tools and commands
- About enhancing productivity while editing
Now that you have your basic layout specified and a line feature created to define the route of the strip map, you need to create a strip map index layer that can be used to define the parameters of each page.