Prerequisite:
A Geometry attribute can be configured on schematic feature classes to retrieve geometry data from any specific SHAPE field related to an ArcGIS feature—that is, to retrieve an x-coordinate, y-coordinate, or list of vertices. Configuring Geometry schematic attribute parameters consists of specifying the type of geometry that needs to be decoded and the field on which the decoding is expected to operate. The steps below explain how to operate these configurations.
To create the schematic attribute itself, you must start with the steps detailed in the Creating attributes on a schematic feature class topic and select Geometry when specifying the attribute Type at step 6. The steps below concern the specific Geometry attribute configurations that are expected to be operated at step 7 in this topic.
When selecting Geometry as the Type for a new schematic attribute, the Properties tab displays as follows: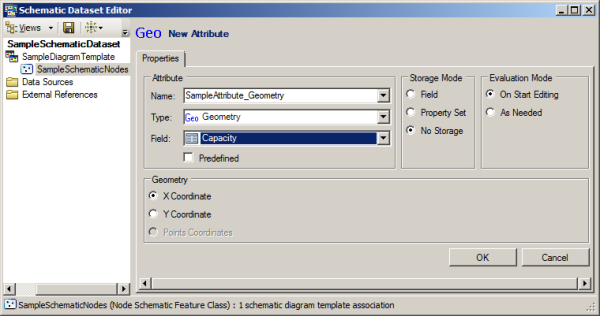
You then have to configure the Geometry attribute parameters as follows:
- Select the field where the geometry data is stored from the Field drop-down list.
Typically, the name of such a binary field in an ArcGIS geodatabase is SHAPE.
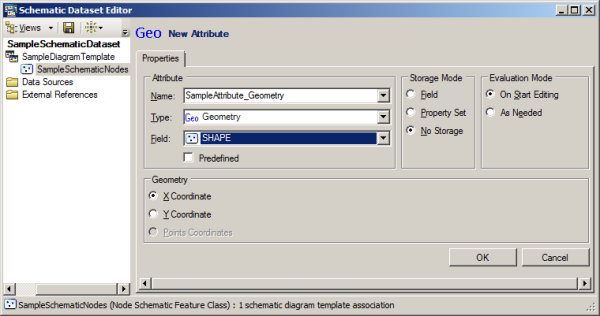
- Choose the geometry type that you want to be automatically decoded on the Geometry section:
- If the Geometry attribute applies to a link schematic feature class, choose Points Coordinates to retrieve the list of vertices.
- If the Geometry attribute applies to a node schematic feature class, either choose X Coordinate to get the x-coordinate position of the schematic feature nodes or choose Y Coordinate to retrieve its y-coordinate position.
To put an endpoint to the Geometry schematic attribute creation, you then need to specify the parameters available in the Storage Mode and Evaluation Mode sections as explained in steps 8 through 11 in the Creating attributes on a schematic feature class topic.