After Geonames data has been loaded into your database and associated with features, you can edit and update the Geonames features as necessary and export them to a text file. This text file is created in Unicode Transfer Format (UTF) in 8-bit or 16-bit format so you can load the Geonames data into data in different locales.
At a minimum, the Geonames feature class must contain the unique feature identifier (UFI) and unique name identifier (UNI) fields. The text file is created for features from the country you choose using the Geonames feature class and table in your geodatabase. It is assumed that the name of the feature class and table are Geonames_FeaturesP and Geonames_Table, respectively, but you can also use Geonames files your organization may have already created.
Fields in the file include the following:
- RC—Region code for the Geonames feature
- UFI—Unique feature identifier for the Geonames feature
- UNI—Unique name identifier for the Geonames feature
- LAT—Latitude of the feature in decimal degrees
- LONG—Longitude of the feature in decimal degrees
- DMS_LAT—Latitude of the feature in degrees, minutes, and seconds
- DMS_LONG—Longitude of the feature in degrees, minutes, and seconds
- UTM—The universal transverse Mercator zone where the feature is located
- JOG—The Joint Operation Graphic used as the source
- FC—The feature classification for the Geonames feature
- DSG—The feature designation code for the Geonames feature
- PC—The populated place classification
- CC1—Primary country code
- ADM1—First-order administrative division for the feature
- ADM2—Secondary-order administrative division for the feature
- DIM—The population or elevation of the place associated with the feature
- POP—A reference to the size of the population of the place associated with the feature
- ELEV—Elevation of the place associated with the feature
- CC2—Secondary country code
- NT—Name type for the feature
- LC—Language code for the place associated with the feature
- SHORT_FORM—The short name of the feature
- GENERIC—The generic name of the feature
- SORT_NAME—The name used to sort the feature
- FULL_NAME—The full name of the place associated with the feature
- FULL_NAME_ND—The full name of the place associated with the feature without diacritics
- MODIFY_DATE—Date and time the feature was last modified
- DISPLAY—Comma-separated numerals such as 1,2,9 where each numeral represents a scale-band to which any particular name feature applies for display
- Start ArcCatalog.
- On the main menu, click Customize > Toolbars > Defense Mapping.
- Select the geodatabase to export the Geonames from in the Catalog tree.
- Click the GDB2Geonames button
 on the Defense Mapping toolbar.
on the Defense Mapping toolbar.
The GDB2Geonames dialog box appears.
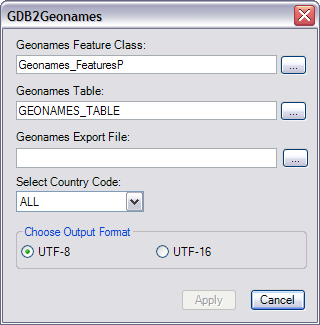
- If necessary, click the ellipsis (...) next to the Geonames Feature Class text box.
The Select Geonames Feature Class dialog box appears.
- Navigate to the feature class that contains your Geonames features.
- Click Add.
The GDB2Geonames dialog box appears with the correct feature class name in the Geonames Feature Class text box.
- If necessary, click the ellipsis (...) next to the Geonames Table text box.
The Select Geonames Table dialog box appears.
- Navigate to the table for your Geonames features.
- Click Add.
The GDB2Geonames dialog box appears with the correct table name in the Geonames Table text box.
- Click the ellipsis (...) next to the Geonames Export File text box.
The Browse to the Geonames output file location dialog box appears.
- Navigate to the directory where you want the text file to be created.
- Type a name for the file in the Name text box.
- Click Save.
The GDB2Geonames dialog box appears with the name of the output file in the Geonames Export File text box.
- Click the Select Country Code drop-down arrow and choose the country code that corresponds with the country for which you want to export Geonames features.
- Choose an output format for the file.
You can use either an 8-bit or 16-bit format.
- Click Apply.
The text file is created. A message appears when the process is complete.
- Click OK.