- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced
Additional library information: Contents, Object Model Diagram
To use the code in this topic, reference the following assemblies in your Visual Studio project. In the code files, you will need using (C#) or Imports (VB .NET) directives for the corresponding namespaces (given in parenthesis below if different from the assembly name):
- ESRI.ArcGIS.CatalogUI
- ESRI.ArcGIS.Catalog
- ESRI.ArcGIS.Framework
- ESRI.ArcGIS.System (ESRI.ArcGIS.esriSystem)
- ESRI.ArcGIS.Carto
- ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry
- System.Windows.Forms
The CatalogUI library provides user interfaces (UI), including property pages, that support objects contained in the Catalog library. In addition to the property pages, there are a number of dialogs, including GxDialog that can be used when interacting with catalogs and their contents. The GxDialog object supports the Add Data functionality of ArcGIS for Desktop applications. FindDialog is also implemented by this library. Many of the commands and context menus in the ArcCatalog application are defined in this library.
Developers extend this library when they create UIs for corresponding components they created in the Catalog library.
See the following sections for more information about this namespace:
GxView
ArcCatalog offers a simple framework for hosting GxViews. GxViews represent different UIs to the various GxObjects. Different GxViews are used for different tasks. The tree view is always available (although it can be shown or hidden at your discretion). The tree view is the primary navigation tool in ArcCatalog and is used to establish the current selection location. The selection location governs what is shown by other GxViews such as GxContentsView or GxGeographicView.
The GxView object is shown in the following diagram:
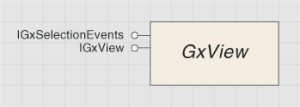
There are two types of views: tabbed and preview. They are implemented in the same way but are registered in separate component categories depending on the look and feel desired. Tabbed views are individual tabs in the ArcCatalog main window. They are always available regardless of the type of the current selection.
Previews are only available on the Preview tab and only display if appropriate for the type of the current selection. This is determined by the Applies method on IGxView. If the view does apply, it is an option in the Preview drop-down combo box. If it does not apply, this option is unavailable. Applies has no effect when the view is registered as a tabbed view.
At appropriate times, ArcCatalog calls Activate and Deactivate on the GxView to inform it that it is becoming active or inactive. In response, the view typically refreshes itself and establishes or releases references to any resources needed for interaction with the user.
GxView must minimally support the IGxView interface, which ArcCatalog uses to negotiate with the view. It asks the view for an hWnd to display through the hWnd property. It represents this hWnd so that it is a child of an ArcCatalog hWnd. It also guarantees events are passed to the hWnd correctly and that it is resized when the ArcCatalog window is resized. To create a custom view, you must implement this interface. Use the Activate method to hold on to the GxApplication and GxCatalog objects that are passed in as parameters. The Deactivate method releases these references.
DefaultToolbarCLSID provides a reference to the default toolbar for the particular view. The default toolbar for a view contains tools that are appropriate for the current type of GxView.
If the SupportsTools property returns true, ArcCatalog intercepts mouse events normally destined for the view and instead sends them to the active tool.
The following code example uses the Name property of the IGxView interface to determine if you are looking at a preview. If you are, then the class ID of the preview is changed to a table view.
[VB.NET] Public Sub IsPreview(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
If UCase(gxView.Name)="PREVIEW" Then
'The above line could be replaced with "If TypeOf gxView Is IGxPreview Then".
Dim pUID As UID=New UIDClass
Dim gxPreview As IGxPreview=CType(gxView, IGxPreview)
MessageBox.Show(CStr(gxPreview.ViewClassID))
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}"
gxPreview.ViewClassID=pUID
End If
End Sub
public void IsPreview(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
if (gxView.Name.ToUpper() == "PREVIEW")
{
//The above line could be replaced with "If TypeOf gxView Is IGxPreview Then".
UID pUID=new UIDClass();
IGxPreview gxPreview=(IGxPreview)gxView;
MessageBox.Show(System.Convert.ToString(gxPreview.ViewClassID));
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}";
gxPreview.ViewClassID=pUID;
}
}
GxViews optionally support the IGxViewPrint interface to allow you to print the current display. This is useful for the metadata view as it allows you to create scripts that print well-formatted metadata for a batch of objects at the same time.
GxContentsView and GxContentsViewColumns
The GxContentsView coclass shows the children of the current selection location in a variety of styles: large icons, list, report, and thumbnails. You can set the style by changing the DisplayStyle property on IGxContentsView. The GxContentsView object is shown in the following diagram:
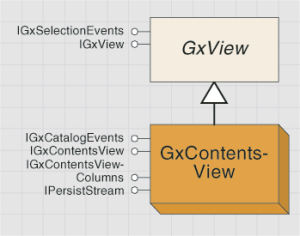
The following code example checks the current view to determine if it is a GxContentsView. This code also accesses properties associated with that view.
[VB.NET] Public Sub IsCurrenntViewGxContentsView(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
Dim gxContentsViewColumns As IGxContentsViewColumns
Dim gxContentsViewColumn As IGxContentsViewColumn
If TypeOf gxView Is IGxContentsViewColumns Then
gxContentsViewColumns=CType(gxView, IGxContentsViewColumns)
gxContentsViewColumn=gxContentsViewColumns.ColumnByIndex(0)
MessageBox.Show(gxContentsViewColumn.Caption & ", " & gxContentsViewColumn.PropertyName)
End If
End Sub
public void IsCurrenntViewGxContentsView(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
IGxContentsViewColumns gxContentsViewColumns=null;
IGxContentsViewColumn gxContentsViewColumn=null;
if (gxView is IGxContentsViewColumns)
{
gxContentsViewColumns=(IGxContentsViewColumns)gxView;
gxContentsViewColumn=gxContentsViewColumns.get_ColumnByIndex(0);
MessageBox.Show(gxContentsViewColumn.Caption + ", " +
gxContentsViewColumn.PropertyName);
}
}
The IGxContentsView interface is implemented by the GxContentsView object. It provides the ability to change how you interact with a view of that type. The types of files displayed, how they are displayed, and whether more than one can be selected at a time are all controlled through this interface.
Constrain the set of objects displayed by supplying an object filter through the ObjectFilter property. For a discussion of available filters and how to create your own, see the sections on GxDialog and GxObjectFilters.
The IGxContentsViewColumns interface serves as a container for the GxContentsViewColumn objects contained in the GxContentsView object. The objects in the collection represent the columns in the tabbed display area of the view (when Contents is the active tab).
After using the InsertColumn method to add a new column, execute the UpdateColumns method to refresh the column list. RemoveAllColumns does not remove the Name and Type columns; these columns cannot be removed. Removing columns does not just affect that session, it is permanent.
GxContentsViewColumn objects represent the columns of information displayed when the Contents tab is the active view. You can create and add columns of information to customize the contents view to display specific information.
The IGxContentsViewColumn interface provides access to the properties of the columns contained in the GxContentsView object. The column properties allow you to set the width, visibility, and caption of the column.
Intrinsic properties (Intrinsic property set to true) are properties such as name, category, and size. These are not useful unless you add a custom GxObject through a new workspace factory; then you can add object-specific special properties.
The PropertyName property is based on keywords in the object metadata. Confirm you have metadata with the specific keyword before using it as a PropertyName.
GxDocumentationView
The metadata view in ArcCatalog is represented by GxDocumentationView. Since it is a GxView, it naturally supports IGxView. To manipulate it, use IGxDocumentationView. This interface allows you to perform the following operations:
- Edit the metadata using a custom editor through the Edit method.
- Edit the metadata properties with a default editor via the EditProperties method.
- Force the metadata to be updated with respect to the object’s current attributes through the Synchronize method.
The GxDocumentationView object is shown in the following diagram:
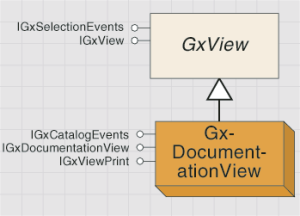
To build a custom editor, create an object that implements the IMetadataEditor interface, then inform the metadata extension object to use it through the IMetadataHelper.Editor property.
GxDocumentationView also implements IGxViewPrint so you can print the well-formatted metadata.
IGxDocumentationView is implemented by GxDocumentationView. It provides a set of methods for manipulating the metadata associated with an object. Through this interface, you can open the editor associated with the metadata, access the metadata properties, and apply the edits made to the metadata.
The following code example brings up the default editor for the metadata associated with the selected object:
[VB.NET] Public Sub OpenDefaultEditor(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
Dim gxDocumentationView As IGxDocumentationView
If TypeOf gxView Is IGxDocumentationView Then
gxDocumentationView=CType(gxView, IGxDocumentationView)
gxDocumentationView.Edit()
End If
End Sub
public void OpenDefaultEditor(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
IGxDocumentationView gxDocumentationView=null;
if (gxView is IGxDocumentationView)
{
gxDocumentationView=(IGxDocumentationView)gxView;
gxDocumentationView.Edit();
}
}
GxGeographicView
Use GxGeographicView to preview your data. It is available through the Preview tab in ArcCatalog. It displays the geography of the selected dataset in its window. By default, the GxGeographicView object is visible on the Preview tab page; however, the object implements IGxView, as do other GxView objects, and can be used as its own tab.
The GxGeographicView object is shown in the following diagram:
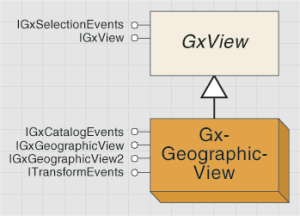
A set of standard manipulation tools is provided for zooming, panning, and performing identifications. You can also add your own tools to work with this view by accessing the Map and MapDisplay properties on the IGxGeographicView interface. Internally, the view uses the services of these two properties to display the selected item, and you can manipulate them as well.
The following code example accesses the geographic view’s map (as IActiveView) and zooms in a fixed amount:
[VB.NET] Public Sub ZoomIn(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
If Not TypeOf gxApplication.View Is IGxPreview Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim gxPreview As IGxPreview=CType(gxApplication.View, IGxPreview)
If Not TypeOf gxPreview.View Is IGxGeographicView Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxPreview.View
Dim gxGeographicView As IGxGeographicView=CType(gxView, IGxGeographicView)
Dim map As IMap=gxGeographicView.Map
Dim activeView As IActiveView=CType(map, IActiveView)
Dim envelope As IEnvelope=activeView.Extent
envelope.Expand(0.75, 0.75, True)
activeView.Extent=envelope
activeView.Refresh()
End Sub
public void ZoomIn(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
if (!(gxApplication.View is IGxPreview))
{
return ;
}
IGxPreview gxPreview=(IGxPreview)gxApplication.View;
if (!(gxPreview.View is IGxGeographicView))
{
return ;
}
IGxView gxView=gxPreview.View;
IGxGeographicView gxGeographicView=(IGxGeographicView)gxView;
IMap map=gxGeographicView.Map;
IActiveView activeView=(IActiveView)map;
IEnvelope envelope=activeView.Extent;
envelope.Expand(0.75, 0.75, true);
activeView.Extent=envelope;
activeView.Refresh();
}
ArcCatalog also supports previewing a map document’s page layout in the geographic view. In this case, you can use the IGxGeographicView2.ActiveView property. It contains a reference to a page layout object if the selected item references a map document (GxMap). You can manipulate this object.
The IGxGeographicView interface is implemented by the GxGeographicView object. It provides access to the map and screen displays that preview the currently selected object. Through this interface, you can retrieve the displayed layer, then use the Map and MapDisplay properties to show additional information in the view.
The DisplayedLayer property is set to Nothing when the selected object cannot be previewed in the GxGeographicView.
The following code example demonstrates how to check for this scenario:
[VB.NET] Public Sub GxGeographicViewDisplayLayer(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
Dim gxPreview As IGxPreview
Dim gxGeographicView As IGxGeographicView
If TypeOf gxView Is IGxPreview Then
gxPreview=CType(gxView, IGxPreview)
If TypeOf gxPreview.View Is IGxGeographicView Then
gxGeographicView=CType(gxPreview.View, IGxGeographicView)
If gxGeographicView.DisplayedLayer Is Nothing Then
MessageBox.Show("Nothing is displayed.")
Else
MessageBox.Show("Something is there.")
End If
End If
End If
End Sub
public void GxGeographicViewDisplayLayer(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
IGxPreview gxPreview=null;
IGxGeographicView gxGeographicView=null;
if (gxView is IGxPreview)
{
gxPreview=(IGxPreview)gxView;
if (gxPreview.View is IGxGeographicView)
{
gxGeographicView=(IGxGeographicView)gxPreview.View;
if (gxGeographicView.DisplayedLayer == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("Nothing is displayed.");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Something is there.");
}
}
}
}
The IGxGeographicView2 interface provides access to the IActiveView interface of the map used to preview the current selection.
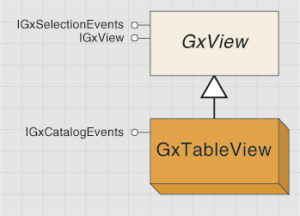
GxTableView and GxTreeView
The GxTableView object is similar to GxGeographicView in that it's used to preview data. By default, it's accessed through the Preview tab. As the name implies, GxTableView is used to preview the table associated with the selected object. The coclass is a type of GxView, so it implements the IGxView interface, but it does not implement additional interfaces.
The GxTableView object is shown in the following diagram:
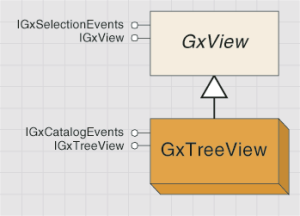
The tree view is represented by GxTreeView; it shows a hierarchical organization of the data holdings as parents and children. It's unlikely you'll need to interact programmatically with the tree view other than to force it to reveal a particular GxObject (through the IGxTreeView.EnsureVisible method) or to initiate a renaming operation (through BeginRename).
The GxTreeView object is shown in the following diagram:
The IGxTreeView interface is implemented solely by the GxTreeView object. It provides the ability to manipulate the object selected in the tree view. You can begin a renaming process, ensure the visibility of the object, or expand the node in the tree view through this interface.
The following code example starts the renaming process for the selected object in the tree view:
[VB.NET] Public Sub BeginRename(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxTreeView As IGxTreeView=gxApplication.TreeView
gxTreeView.BeginRename()
'Add your code here.
End Sub
public void BeginRename(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxTreeView gxTreeView=gxApplication.TreeView;
gxTreeView.BeginRename();
//Add your code here.
}
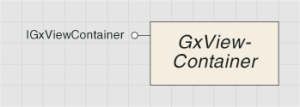
GxViewContainer
The GxViewContainer is an abstract object that permits a GxView object to be a container for additional views. The GxPreview coclass is the only type of GxViewContainer object currently implemented in ArcCatalog. Out of the box, the GxPreview object contains the GxGeographicView and GxTableView objects. This functionality is exposed in the UI through the Geography and Table options on the Preview tab in ArcCatalog.
The GxViewContainer object is shown in the following diagram:
The IGxViewContainer interface provides access to the views within the container. You cannot add views to the container through this interface. Additional views must be added by registering a component in the ESRI GxPreviews category.
The Views property returns an enumeration of the valid views in the container for the currently selected object.
The following code example demonstrates how to find the table view through the IGxViewContainer interface when the Preview tab is active:
[VB.NET] Public Sub FindTableView(application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
If TypeOf gxView Is IGxViewContainer Then
Dim pUID As UID=New UID
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}"
Dim gxViewContainer As IGxViewContainer=CType(gxView, IGxViewContainer)
Dim gxView_Found As IGxView=gxViewContainer.FindView(pUID, False)
If gxView_Found Is Nothing Then
MessageBox.Show("Could not find it.")
End If
End If
End Sub
public void FindTableView(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
if (gxView is IGxViewContainer)
{
UID pUID=new UID();
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}";
IGxViewContainer gxViewContainer=(IGxViewContainer)gxView;
IGxView gxView_Found=gxViewContainer.FindView(pUID, false);
if (gxView_Found == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("Could not find it.");
}
}
}
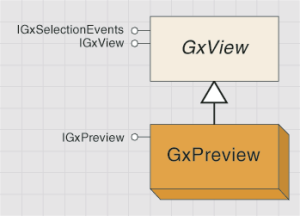
GxPreview
The GxPreview coclass is the only type of GxView that is also a type of GxViewContainer. The class is implemented as a tab in ArcCatalog, but within that tab is a container for additional views. These views provide previews of the selected object, depending on which are applicable. For example, the geography and table previews are available for a shapefile, while only the table preview is available for a table.
The GxPreview object is shown in the following diagram:
The IGxPreview interface is implemented by the GxPreview object. It provides access to the supported views for the selected object. Use this interface to find the supported views, or to retrieve or set the current view.
The ViewClassID property sets and retrieves the current view through its user identification (UID). Setting the UID is the only way to change the current view in the GxPreview object.
The following code example updates the ViewClassID to the GxTableView preview. (In your code, ensure that GxTableView is one of the supported views before setting the property.)
[VB.NET] Public Sub UpdateViewClassID(ByVal application As IApplication)
Dim gxApplication As IGxApplication=CType(application, IGxApplication)
Dim gxView As IGxView=gxApplication.View
If TypeOf gxView Is IGxPreview Then
Dim pUID As UID=New UID
Dim gxPreview As IGxPreview=CType(gxView, IGxPreview)
MessageBox.Show(CStr(gxPreview.ViewClassID))
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}" 'GUID for GxTableView
gxPreview.ViewClassID=pUID
End If
End Sub
public void UpdateViewClassID(IApplication application)
{
IGxApplication gxApplication=(IGxApplication)application;
IGxView gxView=gxApplication.View;
if (gxView is IGxPreview)
{
UID pUID=new UID();
IGxPreview gxPreview=(IGxPreview)gxView;
MessageBox.Show(System.Convert.ToString(gxPreview.ViewClassID));
pUID.Value="{9C34344D-99DC-11D2-AF6A-080009EC734B}"; //GUID for GxTableView
gxPreview.ViewClassID=pUID;
}
}
GxDialog
The GxDialog object controls the browser functionality of ArcCatalog. For example, when you right-click a dataset, point to Import, and click Coverage to Geodatabase, the GxDialog object is employed in the browser that opens, allowing you to select a coverage.
The GxDialog object can be used in ArcCatalog and ArcMap to provide browser capabilities. The Intersect sample tool provides the capability to intersect two layers in the map and create a new geodatabase layer or a shapefile. The GxDialog object is used in that tool to browse to a location to create the layer or shapefile. The available options in a GxDialog browser are based on the filters (GxObjectFilter) held by the object. The GxDialog object maintains a collection of these filters, and you can create a custom filter as well.
The IGxDialog interface is implemented by the GxDialog object and provides access to the dialog box object properties and methods for displaying the dialog box during open or save operations. Use this interface to access the dialog box properties or to display the dialog box for input from the end user.
ObjectFilter returns the active filter in the dialog box. If the dialog box is not open (through DoModalOpen or DoModalSave), this property returns the default filter.
The GxDialog object implements the IGxObjectFilterCollection interface. It provides access to the set of filters used by the GxDialog object. A collection of filters can be attached to a GxDialog object; however, only one filter is active at a time. The active filter is specified through the dialog box when DoModalOpen or DoModalSave is executed through the IGxDialog interface. Use the IGxObjectFilterCollection interface to remove all filters or to add a filter to the object.
The following code example demonstrates how to use the IGxObjectFilterCollection interface to add existing filters to a GxDialog object:
[VB.NET] Public Sub AddExisitingFilters()
Dim enumGxObject As IEnumGxObject=Nothing
Dim gxObjectFilter_Shapefiles As IGxObjectFilter=New GxFilterShapefilesClass
Dim gxObjectFilter_Layers As IGxObjectFilter=New GxFilterLayersClass
Dim gxDialog As IGxDialog=New GxDialogClass
Dim gxObjectFilterCollection As IGxObjectFilterCollection=CType(gxDialog, IGxObjectFilterCollection)
gxObjectFilterCollection.AddFilter(gxObjectFilter_Shapefiles, False)
gxObjectFilterCollection.AddFilter(gxObjectFilter_Layers, True) 'GxObjectFilter_Layers is the default filter.
gxDialog.Title="Browse Data"
gxDialog.DoModalOpen(0, enumGxObject)
End Sub
public void AddExisitingFilters()
{
IEnumGxObject enumGxObject=null;
IGxObjectFilter gxObjectFilter_Shapefiles=new GxFilterShapefilesClass();
IGxObjectFilter gxObjectFilter_Layers=new GxFilterLayersClass();
IGxDialog gxDialog=new GxDialogClass();
IGxObjectFilterCollection gxObjectFilterCollection=(IGxObjectFilterCollection)
gxDialog;
gxObjectFilterCollection.AddFilter(gxObjectFilter_Shapefiles, false);
gxObjectFilterCollection.AddFilter(gxObjectFilter_Layers, true);
//GxObjectFilter_Layers is the default filter.
gxDialog.Title="Browse Data";
gxDialog.DoModalOpen(0, out enumGxObject);
}
Metadata editing
Metadata is edited from the Description tab. It edits ArcGIS metadata. Metadata is authored in a format that is appropriate for the current ArcGIS metadata style, which is determined by the metadata style setting in the Options dialog box in your ArcGIS application. See A quick tour of creating and editing metadata and Editing metadata in the ArcGIS Desktop Help system for details.
The DefaultEditor object provides the capability to add enclosures to an ArcGIS item’s metadata in the same way that attachments can be added to an email message. It can be opened by clicking the Metadata Properties button on the Metadata toolbar in ArcCatalog.
In ArcGIS Desktop 9.3.1 and earlier releases, metadata could be edited using the FGDC metadata editor and an ISO metadata editing wizard. These applications edited metadata that was stored in specific metadata formats, the FGDC XML format and the ESRI-ISO XML format, respectively. These applications are no longer provided with ArcGIS.
The IMetadataEditor interface continues to be supported and is available programmatically. Custom objects that implement this interface will continue to work if you author code to programmatically create the objects and call the Edit method. A custom metadata editor can be written to provide support for directly editing a custom metadata XML format. Custom metadata editor objects do not have to be registered in the Metadata Editors component category—this category is no longer used.
SearchEngine
The following search engines are supplied in ArcCatalog, which allow ArcCatalog to find data:
- CatalogSearchEngine lets you search for any object that appears in ArcCatalog, including objects that are stored in geodatabases. It is the default search engine.
- FileSystemXmlSearchEngine lets you search for file-based objects stored on disk for which metadata has been created. It is faster than CatalogSearchEngine.
You can build a custom search engine by creating a class that implements ISearchEngine and registering it with the Component Categories Manager utility in the ESRI GX Search Engines category. You might do this to support a custom search application that communicates with metadata stored in a relational database rather than in XML files on disk.
