 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
Provides access to the associated query definition.
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 |
CopyLocally | Indicates if the data must be copied locally. |
 |
PrimaryKey | The primary key field names. |
 |
QueryDef | QueryDef of feature class name. |
| Interfaces | Description |
|---|---|
| IQueryName | Provides access to the associated query definition. |
| Classes | Description |
|---|---|
| FeatureQueryName | Esri Feature Query Name object. |
| TableQueryName | Esri Table Query Name object. |
This interface extends the IQueryName interface to allow Objects in tables created from a QueryDef. The table used in the QueryDef does not need to be registered with the geodatabase in order for the table generated from the QueryDef to have Object ID's. An Object ID column is required for a table to support selections. If the QueryDef includes a geometry column, a FeatureClass is created when the name object is opened.
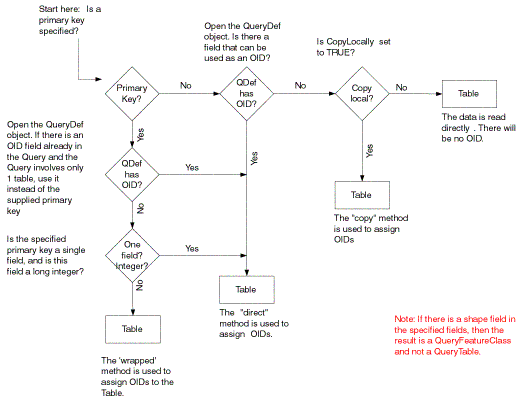
How the PrimaryKey and CopyLocally properties are set determines whether or not the table will have an Object ID column. The following describes the various scenarios:
There are three ways in which Object ID's are assigned to a table:
Direct - The values from the primary key field are used directly as Object ID's. Here the primary key must be a single field and of integer type.
public void IQueryName2_Direct(IWorkspace workspace)
{
IFeatureWorkspace featureWorkspace = (IFeatureWorkspace)workspace;
IQueryDef queryDef = featureWorkspace.CreateQueryDef();
queryDef.SubFields = "*";
queryDef.Tables = "parcels, house_listings";
queryDef.WhereClause = "parcel.parcel_id = house_listing.parcel_id";
//Direct
IQueryName2 queryName2 = new TableQueryNameClass();
queryName2.PrimaryKey = "parcel.parcel_id";
queryName2.QueryDef = queryDef;
}
Wrapped - The primary key values are mapped to unique integer values which are used as the Object ID's. The primary key in this case is set to a list of fields (i.e. composite keys) or a single non-integer field. Two mapping tables are created in memory (Object ID-> PrimaryKey, PrimaryKey-> Object ID). If the tables are too large to fit in memory, virtual memory will be used.
public void IQueryName2_Wrapped(IWorkspace workspace)
{
IFeatureWorkspace featureWorkspace = (IFeatureWorkspace)workspace;
IQueryDef queryDef = featureWorkspace.CreateQueryDef();
queryDef.SubFields = "*";
queryDef.Tables = "parcels, house_listings";
queryDef.WhereClause = "parcel.parcel_id = house_listing.parcel_id";
//Wrapped
IQueryName2 queryName2 = new TableQueryNameClass();
queryName2.PrimaryKey = "parcel.rout_id, parcel.parcel_id";
queryName2.QueryDef = queryDef;
}
Copy - No primary key is set and CopyLocally is set to True. In this case, the table is copied into the scratch workspace and an Object ID field is appended. The scratch workspace is usually under your system temp directory in a file named mx<n>.mdb.
public void IQueryName2_Copy(IWorkspace workspace)
{
IFeatureWorkspace featureWorkspace = (IFeatureWorkspace)workspace;
IQueryDef queryDef = featureWorkspace.CreateQueryDef();
queryDef.SubFields = "*";
queryDef.Tables = "parcels, house_listings";
queryDef.WhereClause = "parcel.parcel_id = house_listing.parcel_id";
//Copy
IQueryName2 queryName2 = new TableQueryNameClass();
queryName2.PrimaryKey = "";
queryName2.CopyLocally = true;
queryName2.QueryDef = queryDef;
}
With copy tables, the fields are renamed (A.field1-> A_field1), but the qualified name is still the alias name.
If you are working with feature classes use FeatureQueryName rather than TableQueryName.
The following diagram illustrates how the criteria described above is used to generate tables from TableQueryNames and FeatureQueryNames:
There are three ways in which Object ID's are assigned to a table:
Direct - The values from the primary key field are used directly as Object ID's. Here the primary key must be a single field and of integer type.
Wrapped - The primary key values are mapped to unique integer values which are used as the Object ID's. The primary key in this case is set to a list of fields (i.e. composite keys) or a single non-integer field. Two mapping tables are created in memory (Object ID-> PrimaryKey, PrimaryKey-> Object ID). If the tables are too large to fit in memory, virtual memory will be used.
Copy - No primary key is set and CopyLocally is set to True. In this case, the table is copied into the scratch workspace and an Object ID field is appended. The scratch workspace is usually under your system temp directory in a file named mx<n>.mdb.
With copy tables, the fields are renamed (A.field1-> A_field1), but the qualified name is still the alias name.
If you are working with feature classes use FeatureQueryName rather than TableQueryName.
The following diagram illustrates how the criteria described above is used to generate tables from TableQueryNames and FeatureQueryNames:

There are three ways in which Object ID's are assigned to a table:
Direct - The values from the primary key field are used directly as Object ID's. Here the primary key must be a single field and of integer type.
Wrapped - The primary key values are mapped to unique integer values which are used as the Object ID's. The primary key in this case is set to a list of fields (i.e. composite keys) or a single non-integer field. Two mapping tables are created in memory (Object ID-> PrimaryKey, PrimaryKey-> Object ID). If the tables are too large to fit in memory, virtual memory will be used.
Copy - No primary key is set and CopyLocally is set to True. In this case, the table is copied into the scratch workspace and an Object ID field is appended. The scratch workspace is usually under your system temp directory in a file named mx<n>.mdb.
With copy tables, the fields are renamed (A.field1-> A_field1), but the qualified name is still the alias name.
If you are working with feature classes use FeatureQueryName rather than TableQueryName.
The following diagram illustrates how the criteria described above is used to generate tables from TableQueryNames and FeatureQueryNames:

IQueryName Interface | IQueryName2 Interface | IQueryName2.CopyLocally Property | FeatureQueryName Class | IQueryName2.PrimaryKey Property | IQueryName2.CopyLocally Property | IQueryName2 Interface | TableQueryName Class