Disponible con una licencia de Geostatistical Analyst.
Some interpolation and simulation methods require the input data to be normally distributed (see Examine the distribution of your data for a list of these methods). The normal score transformation (NST) is designed to transform your dataset so that it closely resembles a standard normal distribution. It does this by ranking the values in your dataset from lowest to highest and matching these ranks to equivalent ranks generated from a normal distribution. Steps in the transformation are as follows: your dataset is sorted and ranked, an equivalent rank from a standard normal distribution is found for each rank from your dataset, and the normal distribution values associated with those ranks make up the transformed dataset. The ranking process can be done using the frequency distribution or the cumulative distribution of the datasets.
Examples showing histograms and cumulative distributions before and after a normal score transformation was applied are shown below:
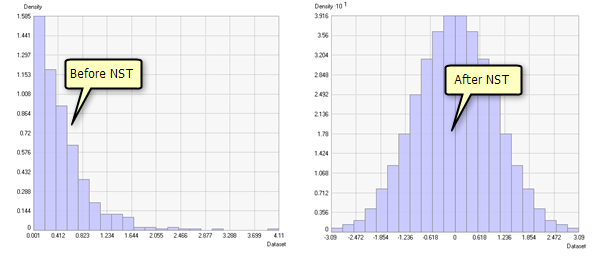
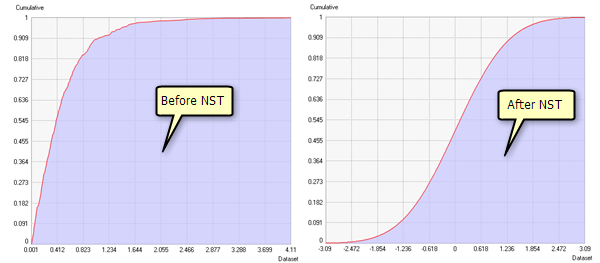
Approximation methods
In Geostatistical Analyst, there are four approximation methods: direct, linear, Gaussian kernels, and multiplicative skewing. The direct method uses the observed cumulative distribution, the linear method fits lines between each step of the cumulative distribution, and the Gaussian kernels method approximates the cumulative distribution by fitting a linear combination of component cumulative normal distributions. Multiplicative skewing approximates the cumulative distribution by fitting a base distribution (Student's t, lognormal, gamma, empirical, and log empirical) that is then skewed by a fitted linear combination of beta distributions (the skewing is done with the inverse probability integral transformation). Lognormal, gamma, and log empirical base distributions can only be used for positive data, and the predictions are guaranteed to be positive. Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) is provided to judge the quality of the fitted model.
After making predictions on the transformed scale, the software automatically transforms the predictions back to the original scale. The choice of approximation method depends on the assumptions you are willing to make and the smoothness of the approximation. The direct method is the least smooth and has the fewest assumptions, and the linear method is intermediate. The Gaussian kernels and multiplicative skewing methods have smooth reverse transformations but assume that the data distribution can be approximated by a finite combination of known distributions.