Récapitulatif
Exporte les nœuds d'un jeu de données TIN vers une classe d'entités ponctuelles.
Illustration
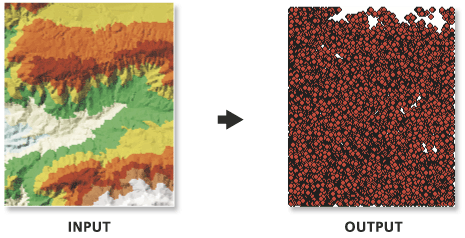
Utilisation
L'indication d'un nom pour le paramètre Champ de valeur entraîne la création d'une classe d'entités points 2D. L'omission de ce nom crée des points 3D.
- Si le TIN possède des valeurs de balise associées à ses triangles, les points peuvent être associés à ces valeurs en indiquant un nom au niveau du paramètre Champ de la valeur portée. Tous les nœuds auxquels aucune valeur de balise n'est attribuée sont définis sur la valeur 0.
Syntaxe
TinNode_3d (in_tin, out_feature_class, {spot_field}, {tag_field})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
in_tin | Jeu de données TIN à traiter. | TIN Layer |
out_feature_class | Classe d'entités qui va être produite par cet outil. | Feature Class |
spot_field (Facultatif) | Nom du champ attributaire d'altitude de la classe d'entités en sortie. Si un nom est fourni, la classe d'entités est en 2D ; sinon, elle est en 3D. Aucun nom n'est fourni par défaut, ce qui entraîne la création d'entités ponctuelles 3D. | String |
tag_field (Facultatif) | Nom du champ attributaire de valeur de balise dans la classe d'entités en sortie. Par défaut, aucun champ de valeur de balise n'est créé. | String |
Exemple de code
1er exemple d'utilisation de l'outil TinNode (fenêtre Python)
L'exemple suivant illustre l'utilisation de cet outil dans la fenêtre Python.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension('3D')
env.workspace = 'C:/data'
arcpy.TinNode_3d('tin', 'elevation_node.shp', '', 'Tag_Value')
2e exemple d'utilisation de l'outil TinNode (script autonome)
L'exemple suivant illustre l'utilisation de cet outil dans un script Python autonome.
"""****************************************************************************
Name: Create Terrain from TIN
Description: This script demonstrates how to create a terrain dataset using
features extracted from a TIN. It is particularly useful in
situations where the source data used in the TIN is not available,
and the amount of data stored in the TIN proves to be too large
for the TIN. The terrain's scalability will allow improved
display performance and faster analysis. The script is designed
to work as a script tool with 5 input arguments.
****************************************************************************"""
# Import system modules
import arcpy
import exceptions, sys, traceback
from arcpy import env
# Set local variables
tin = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0) # TIN used to create terrain
gdbLocation = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1) # Folder that will store terran GDB
gdbName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2) # Name of terrain GDB
fdName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(3) # Name of feature dataset
terrainName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # Name of terrain
try:
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Create the file gdb that will store the feature dataset
arcpy.management.CreateFileGDB(gdbLocation, gdbName)
gdb = '{0}/{1}'.format(gdbLocation, gdbName)
# Obtain spatial reference from TIN
SR = arcpy.Describe(tin).spatialReference
# Create the feature dataset that will store the terrain
arcpy.management.CreateFeatureDataset(gdb, fdName, SR)
fd = '{0}/{1}'.format(gdb, fdName)
# Export TIN elements to feature classes for terrain
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN footprint to define terrain boundary...")
boundary = "{0}/boundary".format(fd)
# Execute TinDomain
arcpy.ddd.TinDomain(tin, tinDomain, 'POLYGON')
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN breaklines...")
breaklines = "{0}/breaklines".format(fd)
# Execute TinLine
arcpy.ddd.TinLine(tin, breaklines, "Code")
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN nodes...")
masspoints = "{0}/masspoints".format(fd)
# Execute TinNode
arcpy.ddd.TinNode(sourceTIN, TIN_nodes)
arcpy.AddMessage("Creating terrain dataset...")
terrain = "terrain_from_tin"
# Execute CreateTerrain
arcpy.ddd.CreateTerrain(fd, terrainName, 10, 50000, "",
"WINDOWSIZE", "ZMEAN", "NONE", 1)
arcpy.AddMessage("Adding terrain pyramid levels...")
terrain = "{0}/{1}".format(fd, terrainName)
pyramids = ["20 5000", "25 10000", "35 25000", "50 50000"]
# Execute AddTerrainPyramidLevel
arcpy.ddd.AddTerrainPyramidLevel(terrain, "", pyramids)
arcpy.AddMessage("Adding features to terrain...")
inFeatures = "{0} Shape softclip 1 0 10 true false boundary_embed <None> "\
"false; {1} Shape masspoints 1 0 50 true false points_embed "\
"<None> false; {2} Shape softline 1 0 25 false false lines_embed "\
"<None> false".format(boundary, masspoints, breaklines)
# Execute AddFeatureClassToTerrain
arcpy.ddd.AddFeatureClassToTerrain(terrain, inFeatures)
arcpy.AddMessage("Building terrain...")
# Execute BuildTerrain
arcpy.ddd.BuildTerrain(terrain, "NO_UPDATE_EXTENT")
arcpy.GetMessages()
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = "PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}"\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = "ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n".format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
finally:
arcpy.CheckInExtension("3D")
Environnements
Informations de licence
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requis 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requis 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requis 3D Analyst