Mit der Spatial Analyst-Lizenz verfügbar.
Zusammenfassung
Ermittelt die Ausrichtung für jede Zelle einer Raster-Oberfläche.
Die Ausrichtung gibt für jeden Ort die Kompassrichtung der Neigung an.
Weitere Informationen zur Funktionsweise des Werkzeugs "Ausrichtung"
Abbildung
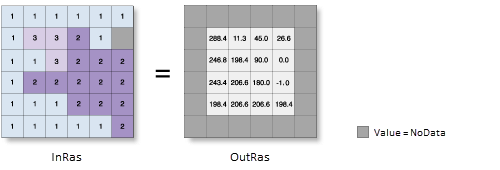
Verwendung
Zur Verarbeitung der Daten verwendet das Werkzeug ein bewegliches Fenster von 3 x 3 Zellen. Wenn der Typ der bearbeiteten Zelle "NoData" lautet, ist die Ausgabe für diese Position "NoData".
Of the eight cells neighboring the processing cell, this tool requires that at least seven of them have a valid value. Wenn weniger als sieben Zellen gültig sind, wird die Berechnung nicht ausgeführt, und die Ausgabe an dieser bearbeiteten Zelle lautet NoData.
The cells in the outermost rows and columns of the output raster will be NoData. Das liegt daran, dass die Zellen entlang der Grenze des Eingabe-Datasets nicht an ausreichend viele andere Zellen angrenzen.
Die Ausrichtung wird als positive Gradangabe von 0 bis 360 ausgedrückt, wobei im Uhrzeigersinn von Norden aus gemessen wird.
Zellen im Eingabe-Raster, die flach sind, d. h. ohne Neigung, wird die Ausrichtung -1 zugewiesen.
For the geodesic method, specifying the surface z-unit is important to ensure the accuracy of the output. The Z unit parameter will be enabled only when the geodesic method is selected.
Wenn im vertikalen Koordinatensystem des Eingabe-Rasters eine Z-Einheit verfügbar ist, wird sie automatisch angewendet. It is suggested that you define a z-unit for the input raster if it is missing. You can use the Define Projection tool to specify a z-unit. If it is undefined, meter will be used by default.
Wenn das Eingabe-Raster neu berechnet werden muss, wird die bilineare Technik verwendet. Ein Eingabe-Raster muss beispielsweise dann neu berechnet werden, wenn das Ausgabe-Koordinatensystem, die Ausdehnung oder die Zellengröße sich von dem entsprechenden Wert der Eingabe unterscheidet.
Dieses Werkzeug lässt sich beim Berechnen der geodätischen Ausrichtung mit GPU beschleunigen. Dies bedeutet, dass sich die Performance der geodätischen Methode verbessern lässt, wenn das System mit einem GPU-Gerät (Grafikprozessor) ausgestattet ist.
The GPU Processing with Spatial Analyst help topic has more details on configuring and working with GPU devices, and some troubleshooting tips should you encounter difficulties.
Weitere Informationen zur Geoverarbeitung von Umgebungen mit diesem Werkzeug finden Sie unter Analyseumgebungen und Spatial Analyst.
Syntax
Aspect (in_raster, {method}, {z_unit})| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
in_raster | Das Eingabe-Oberflächen-Raster. | Raster Layer |
method (optional) | Determines whether to calculate the aspect based on a planar (flat earth) or a geodesic (ellipsoid) method.
The planar method is appropriate to use on local areas in a projection that maintains correct distance and area. It is suitable for analysis that cover areas such cities, counties, or smaller states in area. The geodesic method produces a more accurate result, at the potential cost of an increase in processing time. | String |
z_unit (optional) | Linear unit of vertical z-values. It is defined by a vertical coordinate system if it exists. If a vertical coordinate system does not exist, the z-unit should be defined from the unit list to ensure correct geodesic computation. By default, Meter would be applied.
| String |
Rückgabewert
| Name | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
| out_raster | Das Ausgabe-Ausrichtungs-Raster. Es weist den Typ "Gleitkomma" auf. | Raster |
Codebeispiel
Aspect – Beispiel 1 (Python-Fenster)
In diesem Beispiel wird ein Ausrichtungs-Raster aus einem Eingabe-Oberflächen-Raster erstellt.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outAspect = Aspect("elevation")
outAspect.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outaspect01.img")
Aspect – Beispiel 2 (eigenständiges Skript)
In diesem Beispiel wird ein Ausrichtungs-Raster aus einem Eingabe-Oberflächen-Raster erstellt.
# Name: Aspect_Ex_02.py
# Description: Derives aspect from a raster surface.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "elevation"
method = "GEODESIC"
zUnit = "FOOT"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute Aspect
outAspect = Aspect(inRaster, method, zUnit)
# Save the output
outAspect.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outaspect02")
Umgebungen
Lizenzinformationen
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Erfordert Spatial Analyst oder 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Erfordert Spatial Analyst oder 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Erfordert Spatial Analyst oder 3D Analyst