データのジェネラライズでは、手間のかかる反復タスクを多数実行します。そのため、自動化を施すのが理想的です。ただし、ジェネラライズは本質的に状況依存型であり主観的であることから自動化が困難になっています。人間の頭脳は、優先順位付けと状況認知との同時履行を得意としています。それと同じことを、一連の個別コマンドでコンピューターに遂行させることのほうがはるかに困難です。
ArcGIS のジオプロセシング環境は、ジェネラライズ フレームワークの確立によく適しています。これは、データ、縮尺、および製品固有の変数を使用して、互いに独立した手順でデータ変換を処理することができるためです。これらの手順は論理的に連結でき、スクリプトまたはモデル内でループさせて複合ワークフローを作成することもできます。この複合ワークフローを一連のデータに適用して、印刷用または画面表示用のマルチスケール データベースを生成できます。さまざまなフィーチャ グループに対してタスクを連続して容易に反復実行することも、その際に複数のパラメーターを数通りに組み合わせて指定することもできます。ワークフロー全体を自動化または細分化し、手動で編集しながら整合チェックできます。
ジェネラライズ タスクの結合によるカートグラフィック ワークフローの生成
データの既定の縮尺よりも小さい縮尺でマップを作成する工程は、ターゲット縮尺、表示仕様 (たとえば、シンボル)、マップの根本的な目的や意図について理解することから始まります。それに続いて、データセットの接続性や特性に影響をおよぼさずに、フィーチャの全体的な数を減らすための操作を実行します。次に、頂点または他のフィーチャの詳細を除去して、個々のフィーチャの複雑さを軽減します。また、フィーチャ属性の複雑さを軽減するには、フィーチャの類似サブカテゴリ同士を組み合わせて同じシンボルを表示に使う方法もあります。マップの作成を開始した後は、データが最終的なシンボルと一緒に最終的な縮尺で表示されるようになり、シンボル表現の競合の検出と解決が可能になります。
次のフローチャートは、ジェネラライズ ワークフローの簡易バージョンを図示したもので、[カートグラフィ] ツールボックスのツールの中から、データをジェネラライズして縮尺を縮小しながら表示を調整するうえで補助になる主なツールも挙げてあります。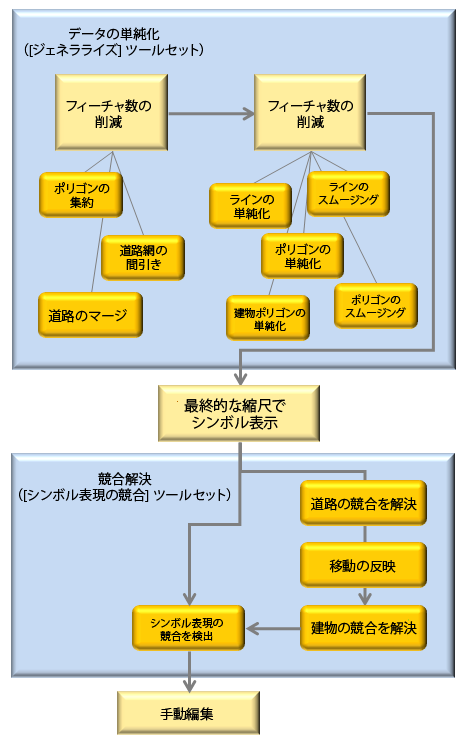
ほとんどのジオプロセシング ツールは通常、出力として新しいデータを生成します。この出力は、以降に実行するツールの入力として使用できます。このことは重要ですので念頭に置いてください。これとは対照的に、地図製作者は、マップ ドキュメント内にすでに確立されているフィーチャ レイヤーの段階的な改良を特徴とするワークフローを利用するのが一般的です。シンボル、レイヤー プロパティ、およびマスキング リレーションシップはすでに定義されているので、入力レイヤーを変更することのほうが望ましいといえます。変更なら、競合解決およびジェネラライズの操作の実行後も、この情報が失われる心配はありません。この理由から、[カートグラフィ] ツールボックスの一部のツールは、データを作成せずに、シンボル表示されたレイヤー内の入力データを変更できるようになっています。この方法が特に扱いやすく効果的となるのは、カートグラフィック リプレゼンテーションと併用する場合です。
リプレゼンテーションによる、ジェネラライズのサポート
リプレゼンテーションは、フィーチャ ジオメトリの代替表示をサポートすることの可能な、ジオデータベース フィーチャクラスのプロパティです。フィーチャクラスは複数のリプレゼンテーションに関連付けることによって、同一データの複数表示をサポートできるようにしています。リプレゼンテーションの果たす役割はジェネラライズに好都合ですが、特定の縮尺 (あるいは小さい縮尺範囲) に対して作成されるフィーチャクラスは 1 つだけであることを念頭に置いてください。このことは、そのフィーチャクラスに関連付けられているリプレゼンテーション数には関係ありません。一連のフィーチャの複数表示をサポートできれば (つまり、リプレゼンテーションを使用して、同じフィーチャを複数の縮尺で描画できれば) という想定は、必然的です。縮尺に若干の変更を行うには、一部のリプレゼンテーション フィーチャの形状を微調整するとうまくいきます。あるいは、その形状の一部を隠す方法でもよいでしょう。しかし、リプレゼンテーションを使用する場合でも 1 対 1 のリレーションシップが存続します。そのため、各フィーチャは 1 つまたは複数の代替表示が可能ですが、新しいフィーチャにフィーチャを結合することは不可能です。たとえば、リプレゼンテーション表示を単独で使用しても、一連の個別の建物を家屋密集地域としてモデル化することはできません。マルチスケールのマッピングを本格的にサポートするには、フィーチャを正しく処理する必要があります。その結果として、フィーチャの密度および詳細が知覚可能なものになるので、シンボル表示の競合を回避できます。これを遂行するのに役立つツールは、[ジェネラライズ] ツールセットおよび [シンボル表現の競合] ツールセットに収録されています。
編集時の振舞いの設定には 2 通りがあり、そのどちらかをリプレゼンテーションに使用できます。編集の設定はリプレゼンテーションのプロパティであり、フィーチャクラスにリプレゼンテーションが作成されたときに確定されます。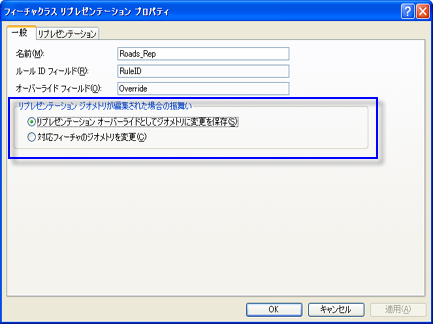
- リプレゼンテーション オーバーライドとしてジオメトリに変更を保存。これがデフォルトです。この設定では、フィーチャのジオメトリに加えた変更内容は、フィーチャクラス属性テーブル内の別個の BLOB フィールドに格納されるので、現在のリプレゼンテーションでしかアクセスできなくなります。Shape フィールドに格納されているフィーチャのベース ジオメトリには、変更が行われません。
- 対応フィーチャのジオメトリを変更。この設定では、フィーチャのジオメトリに変更を加えると、フィーチャクラスの実際の Shape フィールドが変更され、フィーチャクラスに関連付けられている他のリプレゼンテーションに影響がおよびます。
一部のジェネラライズ ツールは、新しくデータセットを作成することなく入力レイヤーを変更します。これは「入/出力派生データ」と呼ばれています。リプレゼンテーションを指すレイヤーを使用する際は、[リプレゼンテーション オーバーライドとしてジオメトリに変更を保存] 設定をオンにすることを強くお勧めします。このことは、グラフィックス競合ツール ([道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)]、[移動の反映 (Propagate Displacement)]、または [建物の競合を解決 (Resolve Building Conflicts)]) を使用して作業する場合に特に当てはまります。これらのツールを実行すると、入力レイヤーのジオメトリが変更されるためです。この設定がオンの場合、これらのツールでフィーチャに加えられた変更内容は、リプレゼンテーションにオーバーライドとして格納されますが、オリジナルのジオメトリは変更されません。この方法で作業したときのメリットは、フィーチャのオリジナルの形状を (Shape フィールドで) 参照して目視で簡単に比較できることや、結果が適切でなければ元に戻すことさえ可能なことです。
また、データをかなり広範にジェネラライズする場合にも、リプレゼンテーションは好都合です。ジェネラライズ処理で直接的に小縮尺を確定して扱えれば面倒がありませんが、通常は中間縮尺が必要になります。暫定的な中間縮尺を経てデータの表示を調整しながら最終的な縮尺を決めるという方法では、精度の低さが誇張されることがあります。これは、詳細データを表示対象から除外する際にいくつかの決定を行う必要があるためです。たとえば、大縮尺のマップにフィーチャ B が収まるように、フィーチャ A を変位させる場合を考えましょう。マップの縮尺が比較的小さい場合、フィーチャ B を表示しきれないので、A が変位したことを確認したり A の派生元を突き止めたりするのは容易ではありません。このような場合、低い精度を求めているのでなければ、次に小さい縮尺を試してください。リプレゼンテーションをオーバーライドすれば、フィーチャの開始場所をすばやく簡単に見た目で判断し、必要に応じて元に戻せるのでこのような状況に役立ちます。
ModelBuilder のジェネラライズ ツールのチェーニング
[ジェネラライズ] ツールには、複数値の入力 (1 つまたは複数のフィーチャクラスのリスト) が利用されます。ジオプロセシング ツール (たとえば、[ユニオン (Union)] ツール) は複数値を受け入れるものが大半を占めていますが、[ジェネラライズ] ツールは複数値の出力も行うという点で特異的です。このため、望みのモデルを生成するには、ModelBuilder の手法を 2 ~ 3 覚える必要があります。これらの方法については、この後で説明します。
複数の入/出力によるツールのチェーニング
[道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツール、[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツール、および [建物の競合を解決 (Resolve Building Conflicts)] ツールの場合、出力は複数値です。つまり、これらのツールの出力を直接使えるのは、複数値の入力を受け入れるツールだけです。たとえば、3 つのレイヤーを [道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールへの入力として使用した場合、間引き後に同じ 3 つのレイヤーを [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールへの入力としても使用したいときは、[道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールの出力を [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールに直接チェーニングするという方法が有効です。![[道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールから [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールに複数の入力をチェーニングします。 [道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールから [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールに複数の入力をチェーニングします。](GUID-7AD47270-6AD8-4071-8154-ED3437C6E1D5-web.png)
別途にレイヤーを複数値に追加するには、[値の収集] ツールを使用します。下の例は、別途 2 つのレイヤーを [道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] の出力に追加して、[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] への入力を作成する方法を示しています。![[値の収集] ツールを使用して、別途の入力を [道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールからの複数値の出力に追加してから、[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールにチェーニングさせます。 [値の収集] ツールを使用して、別途の入力を [道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールからの複数値の出力に追加してから、[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールにチェーニングさせます。](GUID-35522A66-F017-4A30-BB9A-DB35D2B41348-web.png)
複数の出力を単一入力にチェーニング
複数値を出力するツールを単一入力の可能なツールにチェーニングさせるには、[アペンド (Append)] ツールを使用して、複数のフィーチャクラスをマージします。このワークフローの例では、[道路網の間引き (Thin Road Network)] ツールで処理された複数の道路入力レイヤーをアペンドして、単一入力だけを受け入れる [道路のマージ (Merge Divided Roads)] ツールへの入力として使用しています。![[アペンド (Append)] ツールを使用して、複数の出力を単一入力に連結 [アペンド (Append)] ツールを使用して、複数の出力を単一入力に連結](GUID-4F328851-5418-4712-BD17-4302FCC28776-web.png)
複数の入力の個別チェーニング
場合によっては、あるツールからの複数出力を個別に別のツールに渡したいことがあります。たとえば、最初のツールからの出力の一部だけを 2 番目のツールに使用したい場合や、2 番目のツールで入力ごとに特定のパラメーターを設定したい場合などです。たとえば、[建物の競合を解決 (Resolve Building Conflicts)] ツールを使用すると、各入力レイヤーをバリアとして定義する方法を十分に制御できます。これらの例では、両方のツールへの入力と同じレイヤーのセットを使用しますが、最初のツールの出力を 2 番目のツールの前提条件として設定し、正しい処理順序が適用されるようにします (下の図を参照)。この手法を適用すると望ましいのは、最初のツール (たとえば [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールなど) で、新しい出力レイヤーの作成は行わずに、入力レイヤーが変更可能な場合です。
下の例では、3 つのトランスポート レイヤーを、両方のツールへの入力として使用しています。これが可能になっている理由は、これらのレイヤー [道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] で変更され、新しい出力フィーチャクラスは作成されないためです。[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールの出力を [建物の競合を解決 (Resolve Building Conflicts)] ツールを処理するための前提条件として使用することによって、[道路の競合を解決 (Resolve Road Conflicts)] ツールの処理が完了してから、[建物の競合を解決 (Resolve Building Conflicts)] ツールを開始できるようになります。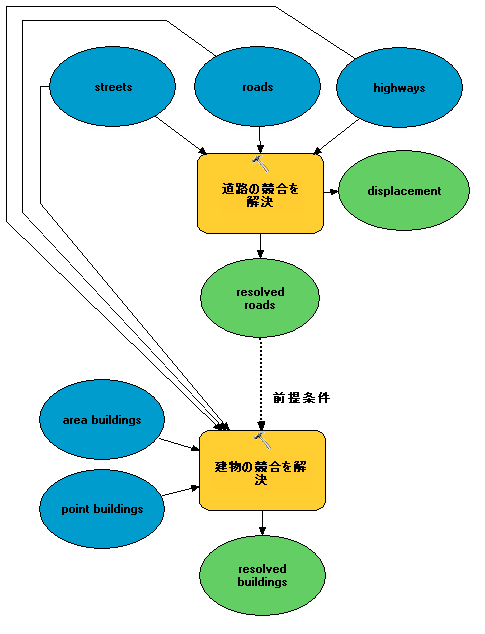
入力のシンボル表示
シンボル表示されたレイヤーだけを受け入れるツール同士をチェーニングさせるには、[フィーチャ レイヤーの作成 (Make Feature Layer)] ツールと [レイヤーのシンボル情報を適用 (Apply Symbology From Layer)] ツールを使用して、ModelBuilder およびスクリプト環境でのチェーニング用途に合わせて出力レイヤーを準備する必要があります。![[フィーチャ レイヤーの作成 (Make Feature Layer)] ツールと [レイヤーのシンボル情報を適用 (Apply Symbology From Layer)] を使用して、ツール間でシンボル情報を受け渡します。 [フィーチャ レイヤーの作成 (Make Feature Layer)] ツールと [レイヤーのシンボル情報を適用 (Apply Symbology From Layer)] を使用して、ツール間でシンボル情報を受け渡します。](GUID-D52CB978-2275-415E-8DF3-D030C5F4A5DE-web.png)
縮尺を縮小しながらデータの表示を調整する Python スクリプト例
カートグラフィ ツールボックスのワークフロー例 (スタンドアロン Python スクリプト)
このスタンドアロン スクリプトは、サンプル ワークフロー全体を通してカートグラフィ ツールボックスのツールをいくつか使用して 1:25,000 の縮尺データをジェネラライズし、シンボル表現の競合を解決して、1:50,000 の縮尺で表示します。
# Name: cartography_workflow_script.py
# Description: Process features in order to resolve graphic conflicts when
# changing scales from 25K to 50K.
#
# Tools used = Aggregate Polygons, Align Marker To Stroke Or Fill, Apply
# Symbology From Layer, Create Overpass, Create Underpass, Calculate
# Line Caps, Eliminate Polygon Part, Make Feature Layer, Merge
# Divided Roads, Propagate Displacement, Resolve Building Conflicts
# Resolve Road Conflicts, Select, Select Layer By Attribute, Set
# Representation Control Point At Intersect, Set Representation
# Control Point By Angle, Simplify Building,Simplify Line, Simplify
# Polygon, Smooth Line, Smooth Polygon, Thin Road Network
# Minimum ArcGIS version = 10
# Author: ESRI
#
# The geodatabase used in this workflow is assumed to be in c:\data
# - please replace this path to your machine specific folder.
# Import system modules
import arcpy, sys, os
from arcpy import env
# Start the processing
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb"
# The data was captured at a scale of 1:24000, and this workflow will produce
# data appropriate for a scale of 1:50000.
# Most of the geoprocessing tools in this workflow require a reference scale
env.referenceScale = "50000"
env.cartographicCoordinateSystem = ""
###############
# HYDROGRAPHY #
###############
# A subset of linear features (rivers/streams) will be processed
# for simplification and smoothing
# A subset of polygonal features (reservoirs/lakes) will be procesed
# for simplification and smoothing
# The workspace is set to the hydrography feature dataset
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb/hydrography"
# Linear hydrographic features
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("streamnetwork", "streamlayer", "", "", "")
# A selection is made for features which are rivers/streams
arcpy.SelectLayerByAttribute_management("streamlayer", "NEW_SELECTION",
'"FCsubtype" = 1')
# In order to reduce the complexity from the streams, vertices are removed using
# the Simplify Line tool
arcpy.SimplifyLine_cartography("streamlayer", "streams_simplified",
"BEND_SIMPLIFY", "100 meters", "RESOLVE_ERRORS")
# In order to reduce the amount or severity of sharp angles, Smooth Line is used
# to improve the shape of the streams
arcpy.SmoothLine_cartography("streams_simplified", "streams",
"BEZIER_INTERPOLATION", "#", "0", 'FLAG_ERRORS')
# Some of the processed features are intermittent rivers or streams and are
# symbolized as dashed lines. When symbolized with representations, the dashes
# can be centered around corners to improve the look of the features. The corners
# are identified as vertices which will be flagged as representation control
# points. Representation symbology is applied to a feature layer in order to be
# processed for control points.
# To place dashes at corners, representation symbology needs to be used by
# the feature layer.
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("streams", "streamslayer", "", "", "")
# Representation symbology is applied to a feature layer in order to be
# processed for control points.
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("streamslayer",
"C:/data/stream_symbols.lyr")
# The dashes in the stream symbol will be placed at control points created
# anywhere an angle is less than (or equal to) 130 degrees.
arcpy.SetRepresentationControlPointByAngle_cartography("streamslayer", "130")
# Polygonal hydrographic features
# A selection is made to create a new feature class for reservoirs.
arcpy.Select_analysis("openwater", "reservoirs", '"FCsubtype" = 4')
# A selection is made to create a separate feature class for processing in order
# to generate lakes.
arcpy.Select_analysis("openwater", "water_select", '"FCsubtype" <> 4')
# In order to reduce the complexity from the lakes, vertices are removed using
# the Simplify Line tool.
arcpy.SimplifyPolygon_cartography("water_select", "water_simplified",
"BEND_SIMPLIFY", "100 meters", "0",
"RESOLVE_ERRORS")
# In order to reduce the amount (or severity) of sharp angles, Smooth Line is
# used to improve the shape of the lakes.
arcpy.SmoothPolygon_cartography("water_simplified", "lakes",
"BEZIER_INTERPOLATION", "0", "", "FLAG_ERRORS")
#############
# RAILROADS #
#############
# Set the workspace to the transportation feature dataset
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb/transportation"
# In order to reduce the complexity from the railroads, vertices are removed
# using the Simplify Line tool.
arcpy.SimplifyLine_cartography("railnetwork", "rail_simplified",
"BEND_SIMPLIFY", "100 meters", "RESOLVE_ERRORS")
# The Merge Divided Roads tool requires symbolized features, so pre-made
# symbology is provided to the feature layer.
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("rail_simplified", "railwaylayer", "", "", "")
# In this workflow, the symbology being applied is Representations
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("railwaylayer",
"C:/data/rail_symbols.lyr")
# The Merge Divided Roads tool will be used to generates single line railroad
# features in place of multiple divided railroad lanes.
arcpy.MergeDividedRoads_cartography("railwaylayer", "level", "25 Meters",
"railways")
# To place markers at corners, representation symbology needs to be used by
# the feature layer.
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("railways", "railwayslayer", "", "", "")
# Representation symbology is applied to a feature layer in order to be
# processed for control points.
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("railwayslayer",
"C:/data/rail_symbols.lyr")
# The tick marks in railroad symbol (markers) will be placed at control points
# created anywhere an angle is less than (or equal to) 130 degrees.
arcpy.SetRepresentationControlPointByAngle_cartography("railwayslayer", "130")
###########
# LANDUSE #
###########
# Set the workspace to the landuse feature dataset
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb/landuse"
# The polygons which represent landcover have holes in them where buildings are
# located. The holes need to be removed so they will not appear after buildings
# have moved. In this example, any hole which is less than 50 percent of the
# feature's area will be removed.
arcpy.EliminatePolygonPart_management("cultural", "urban_area", "PERCENT", "0",
"50", "CONTAINED_ONLY")
##############
# BOUNDARIES #
##############
# The boundary features have dashed outlines which are not in phase with each
# other on shared edges between features. To make the dashed outlines in phase
# with each other, representation control points are added wherever features
# share coincident vertices. The control points are then added to the features
# symbolized with Representations.
arcpy.SetRepresentationControlPointAtIntersect_cartography
("C:/data/boundaries.lyr", "C:/data/boundaries.lyr")
#########
# ROADS #
#########
# Set the workspace to the transportation feature dataset
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb/transportation"
# Linear features
# Roads which are dead ends (or cul-de-sacs) should have their Line ending
# property set to BUTT.
arcpy.CalculateLineCaps_cartography("C:/data/road_symbols.lyr", "BUTT",
"CASED_LINE_DANGLE")
# Thin Road Network identifies a subset of road segments that can be removed from
# the display to create a simplified road network that retains the connectivity
# and general character of the input collection. Features are flagged for removal
# when their attribute value in the "invisible" field equals one. A layer
# definition query can be used to display the resulting simplified feature class.
arcpy.ThinRoadNetwork_cartography("roadnetwork", "500 meters", "invisible",
"level")
# The Merge Divided Roads tool will be used to generates single line road
# features in place of multiple divided road lanes.
arcpy.MergeDividedRoads_cartography("C:/data/road_symbols.lyr", "level",
"25 meters", "roads")
# The Resolve Road Conflicts tool requires symbolized features, so pre-made
# symbology is provided to the feature layer.
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("roads", "roadslayer", "", "", "")
# In this workflow, the symbology being applied is Representations
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("roadslayer",
"C:/data/road_symbols.lyr")
# The Resolve Road Conflicts tool does not produce output road layers but instead
# alters the source feature classes of the input road layers. The Resolve Road
# Conflicts tool adjusts line features to ensure that they are graphically
# distinguishable when symbolized at output scale.
arcpy.ResolveRoadConflicts_cartography
("roadslayer", "level", "C:/data/cartography.gdb/buildings/displacement")
# The dashes in the road symbols will be placed at control points created
# anywhere an angle is less than (or equal to) 130 degrees.
arcpy.SetRepresentationControlPointByAngle_cartography("roadslayer", "130")
# Create bridges
# The Create Overpass tool will create a bridge for the roads and a mask for the
# streams wherever a road goes over a steam.
arcpy.CreateOverpass_cartography("roadslayer", "streamslayer", "2 points",
"1 points", "over_mask_fc", "over_mask_rc",
'"BridgeCategory" = 1', "bridges",
"ANGLED", "1 points")
# Create tunnels
# The Create Overpass tool will create a tunnel for the railroads and a mask for
# the railroads wherever a railroad goes under a road.
arcpy.CreateUnderpass_cartography("roadslayer", "railwayslayer", "2 points",
"1 points", "under_mask_fc", "under_mask_rc",
'"RelationshipToSurface" = 3', "tunnels",
"ANGLED", "1 points")
#############
# BUILDINGS #
#############
# Set the workspace to the buildings feature dataset
env.workspace = "C:/data/cartography.gdb/buildings"
# Point features
# When the road features were adjusted by the Resolve Road Conflicts tool, the
# spatial relationship with nearby buildings was affected. A displacement feature
# class was created by that tool in order to record the change applied to the
# roads. This information can be used by the Propagate Displacement tool to apply
# the same change to the point buildings.
# The road displacement is propagated to the point buildings
arcpy.PropagateDisplacement_cartography("point_bldg", "displacement", "AUTO")
# Point buildings will be rotated against nearby linear roads
# The Align Markers To Stroke Or Fill tool can do this with features symbolized
# with Representations.
# A feature layer is made for point buildings
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("point_bldg", "bldglayer", "", "", "")
# The symbology is switched to Representations
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("bldglayer", "C:/data/bldg_symbols.lyr")
# The Align Marker to Stroke Or Fill tool is used to align point buildings to
# face road features within 5 points of the buildings
arcpy.AlignMarkerToStrokeOrFill_cartography("bldglayer", "roadslayer",
"5 points", "PERPENDICULAR")
# Polgyonal features
# When the road features were adjusted by the Resolve Road Conflicts tool, the
# spatial relationship with nearby buildings was affected. A displacement
# feature class was created by that tool in order to record the change applied
# to the roads. This information can be used by the Propagate Displacement tool
# to apply the same change to the polygonal buildings.
# The road displacement is propagated to polygon buildings
arcpy.PropagateDisplacement_cartography("footprints", "displacement", "SOLID")
# A selection is made to create a feature class with buildings larger than
# a minimum size
# The small buildings are not appropriate at the new map scale of 1:50,000
arcpy.Select_analysis("footprints", "buildings_select", '"Shape_Area" > 100')
# There is a need to create better spacing between polygon buildings and combine
# them when they share edges or are very close together
# The Aggregate Polygons tool is used to accomplish this task
arcpy.AggregatePolygons_cartography("buildings_select", "large_buildings",
"20 meters", "", "", "ORTHOGONAL")
# In order to reduce the complexity of the buildings, indentations, extensions
# and extra vertices are removed using the Simplify Building tool.
# Buildings require less visible detail at the new scale of 1:50,000.
arcpy.SimplifyBuilding_cartography("large_buildings", "area_bldg", "20 meters",
"0 unknown", "CHECK_CONFLICTS")
# All buildings require further improvements to achieve better spacing between
# themselves and other nearby features. At the new scale of 1:50,000 the
# symbolized buildings may overlap other features and create a visually congested
# map. To improve the visual congestion, the Resolve Building Conflicts tool is
# used. Buildings are improved in the context of their surrounding features.
# These features are considered barriers to buildings. The Resolve Building
# Conflicts tool requires symbolized features and has several options available
# to improve the buildings. Options include: moving or resizing the buildings,
# orienting or snapping the buildings to nearby features, as well as making the
# buildings invisible. Buildings from multiple feature classes can be used as
# inputs to the tool. Barriers from multiple feature classes can be used as
# inputs to the tool. For each barrier, the option is available to specify a snap
# or orient action for the buildings when they are within a specified distance.
# For each barrier, the option is available to specify a minimum distance for
# buildings to maintain between them.
# A feature layer is made for the polygon buildings
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management("area_bldg", "footprintlayer", "", "", "")
# The symbology is switched to Representations
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("footprintlayer",
"C:/data/footprint_symbols.lyr")
# The Resolve Building Conflicts tool is run with point and polygon buildings
# against roads, streams and railroads. The buildings will be moved away from
# streams and railroads until they reach a minimum distance. The buildings
# within a maximum distance from the roads will be rotated. Further movement
# and rotation may still be required by the tool in order to resolve any
# remaining graphic conflict.
arcpy.ResolveBuildingConflicts_cartography("footprintlayer; bldglayer", "invisible",
"'roadslayer' 'true' '5 meters';'streamslayer' 'false' '5 meters';'railwayslayer' 'false' '10 meters'",
"10 meters", "20 meters", "level")