Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Calculates a magnitude-per-unit area from point features that fall within a neighborhood around each cell.
Illustration
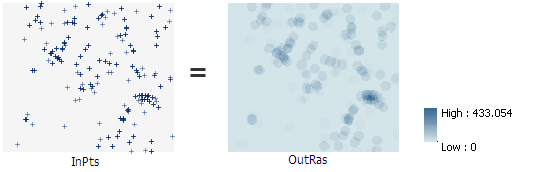
Usage
Larger values of the radius parameter produce a more generalized density raster. Smaller values produce a raster that shows more detail.
Only the points that fall within the neighborhood are considered when calculating the density. If no points fall within the neighborhood at a particular cell, that cell is assigned NoData.
If the area unit scale factor units are small, relative to the distance between the points, the output raster values may be small. To obtain larger values, use the area unit scale factor for larger units (for example, square kilometers versus square meters).
The values on the output raster will always be floating point.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
PointDensity (in_point_features, population_field, {cell_size}, {neighborhood}, {area_unit_scale_factor})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_point_features | The input point features for which to calculate the density. | Feature Layer |
population_field | Field denoting population values for each point. The population field is the count or quantity to be used in the calculation of a continuous surface. Values in the population field may be integer or floating point. The options and default behaviors for the field are listed below.
| Field |
cell_size (Optional) | The cell size for the output raster dataset. This is the value in the environment if specifically set. If the environment is not set, then cell size is the shorter of the width or height of the output extent in the output spatial reference, divided by 250. | Analysis Cell Size |
neighborhood (Optional) | Dictates the shape of the area around each cell used to calculate the density value. This is a Neighborhood class. There are four types of neighbourhood class: NbrAnnulus, NbrCircle, NbrRectangle, and NbrWedge. The forms and descriptions of the classes are:
The default is NbrCircle, where radius is the shortest of the width or height of the output extent in the output spatial reference, divided by 30. | Neighborhood |
area_unit_scale_factor (Optional) | The desired area units of the output density values. A default unit is selected based on the linear unit of the output spatial reference. You can change this to the appropriate unit if you wish to convert the density output. Values for line density convert the units of both length and area. If no output spatial reference is specified, the output spatial reference will be the same as the input feature class. The default output density units is determined by the linear units of the output spatial reference as follows. If the output linear units are meters, the output area density units will be set to SQUARE_KILOMETERS, outputting square kilometers for point features or kilometers per square kilometers for polyline features. If the output linear units are feet, the output area density units will be set to SQUARE_MILES. If the output units is anything other than feet or meters, the output area density units will be set to SQUARE_MAP_UNITS. That is, the output density units will be the square of the linear units of the output spatial reference. For example, if the output linear units is centimeters, the output area density units will be SQUARE_MAP_UNITS, which would result in square centimeters. If the output linear units is kilometers, the output area density units will be SQUARE_MAP_UNITS, which would result in square kilometers. The available options and their corresponding output density units are the following:
| String |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output point density raster. It is always a floating point raster. | Raster |
Code Sample
PointDensity example 1 (Python window)
This example calculates a density raster from a point shape file.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
pdensOut = PointDensity("rec_sites.shp", "NONE", 60, NbrCircle(2500, "MAP"))
pdensOut.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/pointdensity")
PointDensity example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example calculates a density raster from a point shape file.
# Name: PointDensity_Ex_02.py
# Description: Calculates a magnitude per unit area from point
# features that fall within a neighborhood around each cell.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "rec_sites.shp"
populationField = "NONE"
cellSize = 60
# Create the Neighborhood Object
radius = 2500
myNbrCirc = NbrCircle(radius, "MAP")
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute PointDensity
outPdens = PointDensity(inFeatures, populationField, cellSize,
myNbrCirc, "SQUARE_KILOMETERS")
# Save the output
outPdens.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outpdens")
Environments
Licensing Information
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst