ArcGIS for Maritime: Charting allows you to define your own unit conversion and rounding rules that the system will honor during production. By default, the solution does not have any unit conversion or rounding rules defined.
Learn more about the product library
Unit conversion
Maritime Charting allows you to define unit conversion rules that the system will honor during production. The unit conversion rule tool is accessible through ArcCatalog.
The unit conversion destination fields in your Nautical Information System (NIS) and production databases are updated to the converted value whenever you attribute certain source fields for a new or existing feature. The destination _UC field stores the rule ID of the unit conversion rule that is associated with the conversion calculation that was used.
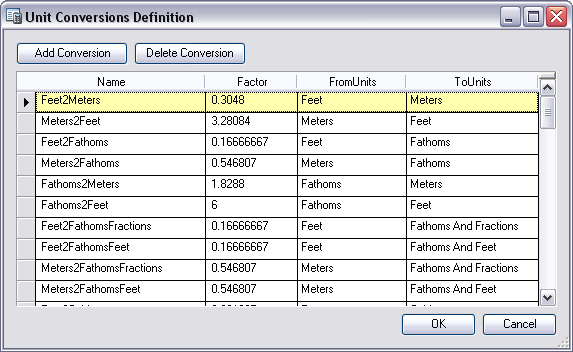
Supported measurements include
- Unknown units
- Inches
- Points
- Feet
- Yards
- Miles
- Nautical Miles
- Millimeters
- Centimeters
- Meters
- Kilometers
- Decimal Degrees
- Decimeters
- Units Last
- Fathoms and Feet
- Fathoms and Fractions
- Degrees of Arc
- Cables
- Fathoms
Rounding rules
Maritime Charting allows you to define unit conversion rounding rules that the system will honor during production. The rounding rule definition tool is accessible through ArcCatalog.
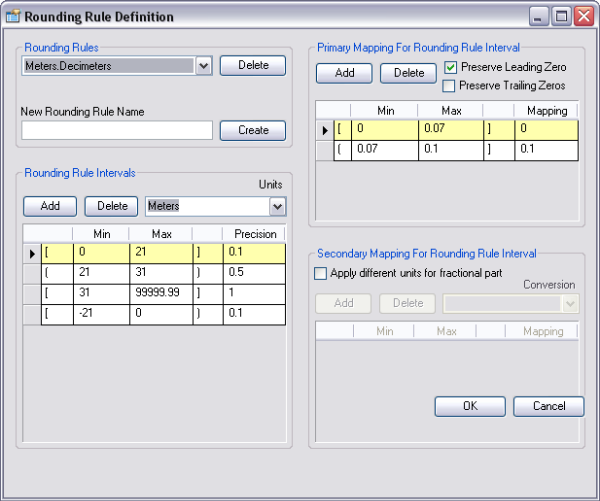
A rounding rule is composed of rounding rule intervals and primary and secondary mappings for each interval.
Rounding rule intervals
A rounding rule interval is defined by ranges of values and a precision. The range of values for the interval specifies a minimum and maximum value. Brackets [ ] are used if you want to include the minimum or maximum in the range; parentheses ( ) exclude the value. The precision defines what the value is rounded to (the nearest 0.1 [tenth], 0.5 [half or whole number], 1 [whole number], and so on).
Some rounding rules may require negative intervals. Soundings, for example, may have drying heights that are represented using negative depths. The drying height values cannot be rounded if a negative interval is not included for the range covered by a minimum value of the highest drying height to a maximum value of zero. Typically, intervals will not pass zero since the mappings associated with negative intervals need to have a negative range, while the mappings associated with positive intervals need to have a positive range.
Primary mappings
A primary mapping is used for comparison in the interval's precision. It is defined by ranges of values and a mapping for each range. The range of values for the interval specifies a minimum and maximum value. Brackets [ ] are used if you want to include the minimum or maximum in the range; parentheses ( ) exclude the value. The mapping defines what the rounded value will be increased to. You can also preserve leading and trailing zeros by checking the appropriate check boxes, which is for labeling/display purposes.
The mappings for negative intervals need to have negative ranges. Such negative mappings are typically symmetric to their positive counterparts. For example: assume the mappings [0.0, 0.07], which maps to 0.0, and (0.07, 1.0], which maps to 1.0. The negative counterpart would be the mappings [-1.0, 0.7), which maps to -1.0, and [-0.7, 0], which maps to 0.0.
For examples using the rules defined in Meters.Decimeters, see the table below.
| Original value | Rounded value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
10.6 | 10.6 | No rounding occurs because the precision is to the tenths decimal place. |
10.64 | 10.6 | 0.04 is compared in the primary mapping and falls between 0 and 0.07, so it is rounded to 0. |
10.68 | 10.7 | 0.08 is compared in the primary mapping and falls between 0.07 and 1, so it is rounded to the next tenth. |
Secondary mappings
A secondary mapping is used when values are in mixed units. It is defined by ranges of values, a conversion rule, and a mapping. The range of values for the interval specifies a minimum and maximum value. Brackets [ ] are used if you want to include the minimum or maximum in the range; parentheses ( ) exclude the value. The mapping defines what the rounded value will be increased to once it is converted.
For examples using the rules defined in Fathoms.Feet, see the table below.
| Original value | Rounded value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
2.55 fathoms | 2 fathoms and 3 feet | 0.55 fathoms is 3.3 feet; 0.3 is compared in the secondary mapping and falls between 0 and 0.7, so it is mapped to 0; 3.3 feet is rounded to 3 feet. |
2.79 fathoms | 2 fathoms and 5 feet | 0.79 fathoms is 4.74 feet; 0.74 is compared in the secondary mapping and falls between 0.7 and 1; it is mapped to 1 and increased to the next whole number; thus 4.74 feet is rounded to 5 feet. |
Rounding rules are referenced, meaning the destination _RR field stores the rule ID of the rounding rule that is associated with the destination field and source unit. However, rounding rules are not applied to the destination field until you specify them to be applied.
Related topics
- Adding a unit conversion rule
- Modifying a unit conversion rule
- Editing data using unit conversion
- Labeling data with unit conversion
- Deleting a unit conversion rule
- Creating a new rounding rule
- Modifying an existing rounding rule interval
- Modifying a primary or secondary mapping for the rounding rule interval
- Deleting a rounding rule
- Deleting a rounding rule interval
- Deleting a primary or secondary mapping