Summary
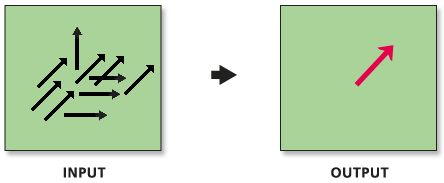
Identifies the mean direction, length, and geographic center for a set of lines.
Illustration
Usage
The input must be a line feature class.
Attribute values for the output line feature(s) include
- CompassA—the compass angle (clockwise from due North)
- DirMean—the directional mean (counterclockwise from due East)
- CirVar—the circular variance (a measure of how much line directions or orientations deviate from the directional mean)
- AveX and AveY—the mean center X and Y coordinates
- AveLen—the mean line length
Analogous to a standard deviation measure, the circular variance (CirVar) value tells how well the directional mean vector represents the set of input vectors. Circular variances range from 0 to 1. If all the input vectors have the exact same (or very similar) directions, the circular variance is small (near 0). When input vector directions span the entire compass, the circular variance is large (near 1).
The Case Field is used to group features for separate linear directional mean computations. When a Case Field is specified, the input line features are first grouped according to case field values, and then an output line feature is created for each group. The case field can be of integer, date, or string type. Records with NULL values for the Case Field will be excluded from analysis.
When measuring direction, the tool only considers the first and last points in a line. The tool does not consider all of the vertices along a line.
-
Map layers can be used to define the Input Feature Class. When using a layer with a selection, only the selected features are included in the analysis.
-
The Output Features is automatically added to the table of contents with default rendering (directional vectors). The rendering applied is defined by a layer file in <ArcGIS>/Desktop10.x/ArcToolbox/Templates/Layers. You can reapply the default rendering, if needed, by importing the template layer symbology.
When this tool runs in ArcMap, the output feature class is automatically added to the Table of Contents (TOC) with default rendering (directional vectors). The rendering applied is defined by a layer file in <ArcGIS>/ArcToolbox/Templates/Layers. You can reapply the default rendering, if needed, by importing the template layer symbology.
Syntax
DirectionalMean_stats (Input_Feature_Class, Output_Feature_Class, Orientation_Only, {Case_Field})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
Input_Feature_Class | The feature class containing vectors for which the mean direction will be calculated. | Feature Layer |
Output_Feature_Class | A line feature class that will contain the features representing the mean directions of the input feature class. | Feature Class |
Orientation_Only |
| Boolean |
Case_Field (Optional) | Field used to group features for separate directional mean calculations. The case field can be of integer, date, or string type. | Field |
Code sample
LinearDirectionalMean Example (Python Window)
The following Python Window script demonstrates how to use the LinearDirectionalMean tool.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = r"C:\data"
arcpy.DirectionalMean_stats("AutoTheft_links.shp", "auto_theft_LDM.shp", "DIRECTION", "#")
LinearDirectionalMean Example (stand-alone Python script)
The following stand-alone python script demonstrates how to use the LinearDirectionalMean tool.
# Measure the geographic distribution of auto thefts
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Local variables...
workspace = "C:/data"
locations = "AutoTheft.shp"
links = "AutoTheft_links.shp"
standardDistance = "auto_theft_SD.shp"
stardardEllipse = "auto_theft_SE.shp"
linearDirectMean = "auto_theft_LDM.shp"
try:
# Set the workspace (to avoid having to type in the full path to the data every time)
arcpy.env.workspace = workspace
# Process: Standard Distance of auto theft locations...
arcpy.StandardDistance_stats(locations, standardDistance, "1_STANDARD_DEVIATION", "#", "#")
# Process: Directional Distribution (Standard Deviational Ellipse) of auto theft locations...
arcpy.DirectionalDistribution_stats(locations, standardEllipse, "1_STANDARD_DEVIATION", "#", "#")
# Process: Linear Directional Mean of auto thefts...
arcpy.DirectionalMean_stats(links, linearDirectMean, "DIRECTION", "#")
except:
# If an error occurred while running a tool, print the messages
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Yes